Prognosis of CKD patients receiving outpatient nephrology care in Italy
- PMID: 21817127
- PMCID: PMC3359552
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01180211
Prognosis of CKD patients receiving outpatient nephrology care in Italy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Prognosis in nondialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients under regular nephrology care is rarely investigated. Design, setting, participants, & measurements We prospectively followed from 2003 to death or June 2010 a cohort of 1248 patients with CKD stages 3 to 5 and previous nephrology care ≥1 year in 25 Italian outpatient nephrology clinics. Cumulative incidence of ESRD or death before ESRD were estimated using the competing-risk approach.
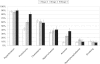
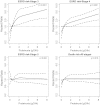
Results: Estimated rates (per 100 patient-years) of ESRD and death 8.3 (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.4 to 9.2) and 5.9 (95% CI 5.2 to 6.6), respectively. Risk of ESRD and death increased progressively from stages 3 to 5. ESRD was more frequent than death in stage 4 and 5 CKD, whereas the opposite was true in stage 3 CKD. Younger age, lower body mass index, proteinuria, and high phosphate predicted ESRD, whereas older age, diabetes, previous cardiovascular disease, ESRD, proteinuria, high uric acid, and anemia predicted death (P < 0.05 for all). Among modifiable risk factors, proteinuria accounted for the greatest contribution to the model fit for either outcome.
Conclusions: In patients receiving continuity of care in Italian nephrology clinics, ESRD was a more frequent outcome than death in stage 4 and 5 CKD, but the opposite was true in stage 3. Outcomes were predicted by modifiable risk factors specific to CKD. Proteinuria used in conjunction with estimated GFR refined risk stratification. These findings provide information, specific to CKD patients under regular outpatient nephrology care, for risk stratification that complement recent observations in the general population.
Figures

References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Keith DS, Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Brown JB, Smith DH: Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch Intern Med 164: 659–663, 2004 - PubMed
-
- O'Hare AM, Choi AI, Bertenthal D, Bacchetti P, Garg AX, Kaufman JS, Walter LC, Mehta KM, Steinman MA, Allon M, McClellan WM, Landefeld CS: Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 2758–2765, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Hallan S, Astor B, Romundstad S, Aasarød K, Kvenild K, Coresh J: Association of kidney function and albuminuria with cardiovascular mortality in older vs younger individuals: The HUNT II study. Arch Intern Med 167: 2490–2496, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Foley R, Murray A, Herzog C, McBean A, Eggers P, Collins A: Chronic kidney disease and the risk for cardiovascular disease, renal replacement, and death in the United States Medicare population, 1998 to 1999. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 489–495, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

