Film excerpts shown to specifically elicit various affects lead to overlapping activation foci in a large set of symmetrical brain regions in males
- PMID: 21818311
- PMCID: PMC3144904
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022343
Film excerpts shown to specifically elicit various affects lead to overlapping activation foci in a large set of symmetrical brain regions in males
Abstract
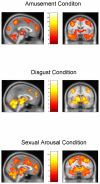
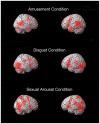
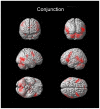
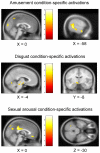
While the limbic system theory continues to be part of common scientific parlance, its validity has been questioned on multiple grounds. Nonetheless, the issue of whether or not there exists a set of brain areas preferentially dedicated to emotional processing remains central within affective neuroscience. Recently, a widespread neural reference space for emotion which includes limbic as well as other regions was characterized in a large meta-analysis. As methodologically heterogeneous studies go into such meta-analyses, showing in an individual study in which all parameters are kept constant, the involvement of overlapping areas for various emotion conditions in keeping with the neural reference space for emotion, would serve as valuable confirmatory evidence. Here, using fMRI, 20 young adult men were scanned while viewing validated neutral and effective emotion-eliciting short film excerpts shown to quickly and specifically elicit disgust, amusement, or sexual arousal. Each emotion-specific run included, in random order, multiple neutral and emotion condition blocks. A stringent conjunction analysis revealed a large overlap across emotion conditions that fit remarkably well with the neural reference space for emotion. This overlap included symmetrical bilateral activation of the medial prefrontal cortex, the anterior cingulate, the temporo-occipital junction, the basal ganglia, the brainstem, the amygdala, the hippocampus, the thalamus, the subthalamic nucleus, the posterior hypothalamus, the cerebellum, as well as the frontal operculum extending towards the anterior insula. This study clearly confirms for the visual modality, that processing emotional stimuli leads to widespread increases in activation that cluster within relatively confined areas, regardless of valence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Areas of brain activation in males and females during viewing of erotic film excerpts.Hum Brain Mapp. 2002 May;16(1):1-13. doi: 10.1002/hbm.10014. Hum Brain Mapp. 2002. PMID: 11870922 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in brain activation to emotional stimuli: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Jun;50(7):1578-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.03.011. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22450197
-
Neural correlates of conscious self-regulation of emotion.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):RC165. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-j0001.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Separate neural networks of implicit emotional processing between pictures and words: A coordinate-based meta-analysis of brain imaging studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Dec;131:331-344. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.041. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34562542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emotional perception: meta-analyses of face and natural scene processing.Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):2524-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.011. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20951215 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional organization of human subgenual cortical areas: Relationship between architectonical segregation and connectional heterogeneity.Neuroimage. 2015 Jul 15;115:177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.053. Epub 2015 May 1. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 25937490 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Role Played by the Default Mode Network during Sexual Stimulation: A Cluster-Based fMRI Meta-Analysis.Behav Sci (Basel). 2024 Jul 5;14(7):570. doi: 10.3390/bs14070570. Behav Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Region- and time- specific effects of ketamine on cerebral blood flow: a randomized controlled trial.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Nov;48(12):1735-1741. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01605-4. Epub 2023 May 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37231079 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mapping the sequence of brain events in response to disgusting food.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Jan;39(1):369-380. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23848. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29024175 Free PMC article.
-
A short review on emotion processing: a lateralized network of neuronal networks.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Mar;227(2):673-684. doi: 10.1007/s00429-021-02331-7. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 34216271 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dalgleish T. The emotional brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:583–589. - PubMed
-
- Murphy FC, Nimmo-Smith I, Lawrence AD. Functional neuroanatomy of emotions: a meta-analysis. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2003;3:207–233. - PubMed
-
- Maclean PD. The limbic system (“visceral brain”) and emotional behavior. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1955;73:130–134. - PubMed
-
- Ledoux J. Emotion and the limbic system concept. Concepts in neuroscience. 1991;2:169–199.
-
- Calder AJ, Lawrence AD, Young AW. Neuropsychology of fear and loathing. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:352–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

