Conformational plasticity of proNGF
- PMID: 21818348
- PMCID: PMC3144226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022615
Conformational plasticity of proNGF
Abstract
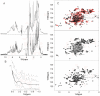
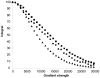
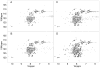
Nerve Growth Factor is an essential protein that supports neuronal survival during development and influences neuronal function throughout adulthood, both in the central and peripheral nervous system. The unprocessed precursor of NGF, proNGF, seems to be endowed with biological functions distinct from those of the mature protein, such as chaperone-like activities and apoptotic and/or neurotrophic properties. We have previously suggested, based on Small Angle X-ray Scattering data, that recombinant murine proNGF has features typical of an intrinsically unfolded protein. Using complementary biophysical techniques, we show here new evidence that clarifies and widens this hypothesis through a detailed comparison of the structural properties of NGF and proNGF. Our data provide direct information about the dynamic properties of the pro-peptide and indicate that proNGF assumes in solution a compact globular conformation. The N-terminal pro-peptide extension influences the chemical environment of the mature protein and protects the protein from proteolytic digestion. Accordingly, we observe that unfolding of proNGF involves a two-steps mechanism. The distinct structural properties of proNGF as compared to NGF agree with and rationalise a different functional role of the precursor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987;237:1154–1162. - PubMed
-
- Chao MV, Bothwell MA, Ross AH, Koprowski H, Lanahan AA, et al. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the human NGF receptor. Science. 1986;232:518–521. - PubMed
-
- He XL, Garcia KC. Structure of nerve growth factor complexed with the shared neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 2004;304:870–875. - PubMed
-
- Wiesmann C, Ultsch MH, Bass SH, de Vos AM. Crystal structure of nerve growth factor in complex with the ligand-binding domain of the TrkA receptor. Nature. 1999;401:184–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

