Targeting oncogenic BRAF in human cancer
- PMID: 21818706
- PMCID: PMC3508196
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2011_162
Targeting oncogenic BRAF in human cancer
Abstract
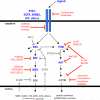
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway activation is a frequent event in human cancer and is often the result of activating mutations in the BRAF and RAS oncogenes. BRAF missense mutations, the vast majority of which are V600E, occur in approximately 8% of human tumors. These kinase domain mutations, which are non-overlapping in distribution with RAS mutations, are observed most frequently in melanoma but are also common in tumors arising in the colon, thyroid, lung, and other sites. Supporting its classification as an oncogene, (V600E)BRAF stimulates ERK signaling, induces proliferation, and is capable of promoting transformation. Given the frequent occurrence of BRAF mutations in human cancer and the continued requirement for BRAF activity in the tumors in which it is mutated, efforts are underway to develop targeted inhibitors of BRAF and its downstream effectors. These agents offer the possibility of greater efficacy and less toxicity than the systemic therapies currently available for tumors driven by activating mutations of MAPK pathway components. Early clinical results with the BRAF-selective inhibitors PLX4032 and GSK2118436 suggest that this strategy will prove successful in a select group of patients whose tumors are driven by oncogenic BRAF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic strategies for inhibiting oncogenic BRAF signaling.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;8(4):419-26. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.06.014. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18644254 Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies for targeting BRAF in human cancer.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2007 May;2(2):121-34. doi: 10.2174/157488707780599393. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2007. PMID: 18473997 Review.
-
Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinase BRAF-mutant lung cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):13456-13461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610456113. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27834212 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Mar;11(3):285-95. doi: 10.2174/187152011795347469. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21426297 Review.
-
The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14903-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008990107. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20668238 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MEK Inhibition in Glioblastoma: Current Perspectives and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 17;26(14):6875. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146875. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interstitial Deletions Generating Fusion Genes.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021 May-Jun;18(3):167-196. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20251. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33893073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric lymphomas and histiocytic disorders of childhood.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2015 Feb;62(1):139-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2014.09.010. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 25435117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors with BRAF mutations.Innovation (Camb). 2024 Oct 18;5(6):100661. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100661. eCollection 2024 Nov 4. Innovation (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39529955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How I treat Langerhans cell histiocytosis.Blood. 2015 Jul 2;126(1):26-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-12-569301. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25827831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–94. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DC. Human melanocyte senescence and melanoma susceptibility genes. Oncogene. 2003;22:3063–9. - PubMed
-
- Bollag G. Overcoming the paradoxical pathway activation of first-generation RAF kinase inhibitors AACR annual meeting; Orlando, FL. 2011.
-
- Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, Burton EA, Wong B, Tsang G, West BL, Powell B, Shellooe R, Marimuthu A, Nguyen H, Zhang KY, Artis DR, Schlessinger J, Su F, Higgins B, Iyer R, D'Andrea K, Koehler A, Stumm M, Lin PS, Lee RJ, Grippo J, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, Chapman PB, Flaherty KT, Xu X, Nathanson KL, Nolop K. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature. 2010;467:596–9. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

