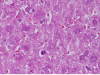
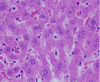
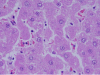
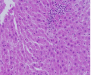
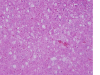
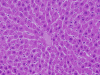
Gold nanoparticles administration induced prominent inflammatory, central vein intima disruption, fatty change and Kupffer cells hyperplasia
- PMID: 21819574
- PMCID: PMC3169478
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-133
Gold nanoparticles administration induced prominent inflammatory, central vein intima disruption, fatty change and Kupffer cells hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: Advances in nanotechnology have identified promising candidates for many biological, biomedical and biomedicine applications. They are being increasingly exploited for medical uses and other industrial applications. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of administration of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) on inflammatory cells infiltration, central vein intima disruption, fatty change, and Kupffer cells hyperplasia in the hepatic tissue in an attempt to cover and understand the toxicity and the potential threat of their therapeutic and diagnostic use.
Methods: A total of 70 healthy male Wistar-Kyoto rats were exposed to GNPs received 50 or 100 μl of GNPs infusion of 10, 20 and 50 nm GNPs for 3 or 7 days. Animals were randomly divided into groups, 12 GNPs-treated rats groups and one control group (NG). Groups 1, 2 and 3 received infusion of 50 μl GNPs of size 10 nm (3 or 7 days), size 20 nm (3 or 7 days) and 50 nm (3 or 7 days), respectively; while groups 4, 5 and 6 received infusion of 100 μl GNPs of size 10 nm, size 20 nm and 50 nm, respectively.
Results: In comparison with respective control rats, exposure to GNPs doses has produced alterations in the hepatocytes, portal triads and sinusoids. The alterations in the hepatocytes were mainly vacuolar to hydropic degeneration, cytopasmic hyaline vacuolation, polymorphism, binucleation, karyopyknosis, karyolysis, karyorrhexis and necrosis. In addition, inflammatory cell infiltration, Kupffer cells hyperplasia, central veins intima disruption, hepatic strands dilatation and occasional fatty change together with a loss of normal architechiture of hepatic strands were also seen.
Conclusions: The alterations induced by the administration of GNPs were size-dependent with smaller ones induced more affects and related with time exposure of GNPs. These alterations might be an indication of injured hepatocytes due to GNPs toxicity that became unable to deal with the accumulated residues resulting from metabolic and structural disturbances caused by these NPs. These histological alterations may suggest that GNPs interact with proteins and enzymes of the hepatic tissue interfering with the antioxidant defense mechanism and leading to reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation which in turn may induce stress in the hepatocytes to undergo necrosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gold nanoparticles induced cloudy swelling to hydropic degeneration, cytoplasmic hyaline vacuolation, polymorphism, binucleation, karyopyknosis, karyolysis, karyorrhexis and necrosis in the liver.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Sep 22;10:166. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-166. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21939512 Free PMC article.
-
Histological alterations in the liver of rats induced by different gold nanoparticle sizes, doses and exposure duration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2012 Jan 25;10:5. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-10-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2012. PMID: 22276919 Free PMC article.
-
Renal tissue alterations were size-dependent with smaller ones induced more effects and related with time exposure of gold nanoparticles.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Sep 21;10:163. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-163. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21936889 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Pathology of the liver sinusoids.Histopathology. 2014 Jun;64(7):907-20. doi: 10.1111/his.12364. Epub 2014 Mar 8. Histopathology. 2014. PMID: 24393125 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of biologically produced gold nanoparticles: toxicity assessment in different rat organs after intraperitoneal injection.AMB Express. 2019 Mar 19;9(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0762-0. AMB Express. 2019. PMID: 30888557 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in proinflammatory and cytotoxic effects of metal nanoparticles.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Apr;99(4):1287-1314. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-03972-x. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39960653 Review.
-
The rheological properties of different GNPs.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Jan 24;11:14. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-14. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22273240 Free PMC article.
-
Gold nanoparticles administration induces disarray of heart muscle, hemorrhagic, chronic inflammatory cells infiltrated by small lymphocytes, cytoplasmic vacuolization and congested and dilated blood vessels.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 9;10:233. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-233. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22151883 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of potential acute cardiotoxicity of biodegradable nanocapsules in rats by intravenous administration.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Oct 5;5(1):168-179. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00207a. eCollection 2016 Jan 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 30090335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu LE, Yung L-YL, Balasubramaniam KS, Hartono D. et al.Translocation and effects of gold nanoparticles after inhalation exposure in rats. Nanotoxicology. 2007;1(3):235–42. doi: 10.1080/17435390701763108. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

