Longitudinal patterns of viremia and oral shedding of rhesus rhadinovirus and retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesviruses in age-structured captive breeding populations of rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)
- PMID: 21819683
- PMCID: PMC3060420
Longitudinal patterns of viremia and oral shedding of rhesus rhadinovirus and retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesviruses in age-structured captive breeding populations of rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)
Abstract
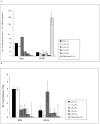
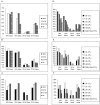
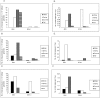
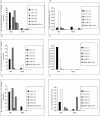
Rhesus rhadinovirus (RRV) and retroperitoneal fibromatosis herpesvirus (RFHV), 2 closely related γ2 herpesviruses, are endemic in breeding populations of rhesus macaques at our institution. We previously reported significantly different prevalence levels, suggesting the transmission dynamics of RRV and RFHV differ with regard to viral shedding and infectivity. We designed a longitudinal study to further examine the previously observed differences between RRV and RFHV prevalence and the potential influence of age, season, and housing location on the same 90 rhesus macaques previously studied. Virus- and host-genome-specific real-time PCR assays were used to determine viral loads for both RRV and RFHV in blood and saliva samples collected at 6 time points over an 18-mo period. Proportions of positive animals and viral load in blood and saliva were compared between and within viruses by age group, location, and season by using 2-part longitudinal modeling with Bayesian inferences. Our results demonstrate that age and season are significant determinants, with age as the most significant factor analyzed, of viremia and oral shedding for both RRV and RFHV, and these pathogens exhibit distinctly different patterns of viremia and oral shedding over time within a single population.
Figures



References
-
- Ackermann M. 2006. Pathogenesis of gammaherpesvirus infections. Vet Microbiol 113:211–222 - PubMed
-
- Animal Welfare Act as Amended 2007. 7 USC §2131-2159.
-
- Applied Biosystems 2008. Guide to performing relative quantitation of gene expression using real-time quantitative PCR. Foster City (CA): Applied Biosystems
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
