Hemodynamic and histologic characterization of a swine (Sus scrofa domestica) model of chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 21819696
- PMCID: PMC3123759
Hemodynamic and histologic characterization of a swine (Sus scrofa domestica) model of chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
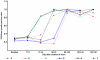
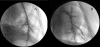
The purpose of this work was to develop and characterize an aortopulmonary shunt model of chronic pulmonary hypertension in swine and provide sequential hemodynamic, angiographic, and histologic data by using an experimental endoarterial biopsy catheter. Nine Yucatan female microswine (Sus scrofa domestica) underwent surgical anastomosis of the left pulmonary artery to the descending aorta. Sequential hemodynamic, angiographic, and pulmonary vascular samples were obtained. Six pigs (mean weight, 22.4±5.3 kg; mean age, 7.3±2.7 mo at surgery) survived long-term (6 mo) and consistently developed marked pulmonary arterial hypertension. Angiography showed characteristic central pulmonary arterial enlargement and peripheral tortuosity and pruning. The biopsy catheter was safe and effective in obtaining pulmonary endoarterial samples for histologic studies, which showed neointimal and medial changes. Autopsy confirmed severe pulmonary vascular changes, including concentric obstructive neointimal and plexiform-like lesions. This swine model showed hemodynamic, angiographic, and histologic characteristics of chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension that mimicked the arterial pulmonary hypertension of systemic-to-pulmonary arterial shunts in humans. Experimental data obtained using this and other models and application of an in vivo endoarterial biopsy technique may aid in understanding mechanisms and developing therapies for experimental and human pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Copyright 2011 by the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science
Figures



References
-
- Beppu H, Ichinose F, Kawai N, Jones RC, Yu PB, Zapol WM, Miyazono K, Li E, Bloch KD. 2004. BMPRII heterozygous mice have mild pulmonary hypertension and an impaired pulmonary vascular remodeling response to prolonged hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L1241–L1247 - PubMed
-
- Berkenbosch JW, Baribeau J, Perreault T. 2000. Decreased synthesis and vasodilation to nitric oxide in piglets with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 278:L276–L283 - PubMed
-
- Bousamra M, 2nd, Rossi R, Jacobs E, Parviz M, Busch C, Nelin LD, Haworth S, Dawson CA. 2000. Systemic lobar shunting induces advanced pulmonary vasculopathy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 120:88–98 - PubMed
-
- Chen EP, Bittner HB, Davis RD, Van Trigt P. 1997. Right ventricular failure—insights provided by a new model of chronic pulmonary hypertension. Transplantation 63:209–216 - PubMed
-
- Chen SJ, Chen IF, Meng QC, Durand J, Dicarlo VS, Oparil S. 1995. Endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan prevents and reverses hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats. J Appl Physiol 79:2122–2131 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
