Phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome 10 is phosphorylated in primary effusion lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma
- PMID: 21819957
- PMCID: PMC3181371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.017
Phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome 10 is phosphorylated in primary effusion lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma
Abstract
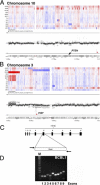
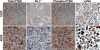
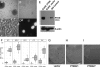
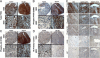
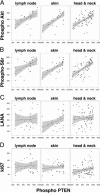
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma driven by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. It is uniquely sensitive to mTOR, PI3K, and Akt inhibitors; however, the basis of this requirement for the mTOR pathway remains to be elucidated. The phosphatase and tensin homolog gene (PTEN) on chromosome 10 controls the first step in the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and is genetically inactivated in many solid tumors. We find an absence of PTEN deletions, mutations, or protein mislocalization in PEL. However, we find consistent hyperphosphorylation at serine 380 of PTEN, which is an inactivating modification, in PEL cell lines and in tumor xenografts. We also evaluated a large tissue microarray of Kaposi's sarcoma biopsies and observed concordant high levels of phospho-PTEN, phospho-Akt, and phospho-S6 ribosomal protein. Reintroduction of PTEN into PEL inhibited colony formation in soft agar, verifying the functional dependence of PEL on PI3K signaling. This was also true for PEL cell lines that carried mutant p53 and for KS-like cell lines. Activating PTEN in these cancers may yield a new treatment strategy for PEL, KS, and similar PTEN wild-type lymphomas.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-126 regulates the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway in SLK cells in vitro and the expression of its pathway members in Kaposi's sarcoma tissue.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(35):e11855. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011855. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30170375 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PI3K/AKT and ERK MAPK signal pathways is required for the induction of lytic cycle replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by herpes simplex virus type 1.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Oct 27;11:240. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-240. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22032493 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mTOR with MLN0128 Overcomes Rapamycin and Chemoresistant Primary Effusion Lymphoma.mBio. 2019 Feb 19;10(1):e02871-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02871-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30782662 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN, more than the AKT pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Jul;28(7):1379-86. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm052. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 17341655 Review.
-
PI3K/AKT Pathway and Its Mediators in Thyroid Carcinomas.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Feb;20(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0175-y. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26597586 Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-positive primary effusion lymphoma tumor formation in NOD/SCID mice is inhibited by neomycin and neamine blocking angiogenin's nuclear translocation.J Virol. 2013 Nov;87(21):11806-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01920-13. Epub 2013 Aug 28. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23986578 Free PMC article.
-
The complete Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genome induces early-onset, metastatic angiosarcoma in transgenic mice.Cell Host Microbe. 2024 May 8;32(5):755-767.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.03.012. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Cell Host Microbe. 2024. PMID: 38653242 Free PMC article.
-
Viral microRNAs Target a Gene Network, Inhibit STAT Activation, and Suppress Interferon Responses.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 19;7:40813. doi: 10.1038/srep40813. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28102325 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibitors block Kaposi sarcoma growth by inhibiting essential autocrine growth factors and tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;73(7):2235-46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1851. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23382046 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-associated cancers.Front Microbiol. 2012 Apr 18;3:141. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00141. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22529843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cesarman E., Chang Y., Moore P.S., Said J.W., Knowles D.M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Matsushima A.Y., Strauchen J.A., Lee G., Scigliano E., Hale E.E., Weisse M.T., Burstein D., Kamel O., Moore P.S., Chang Y. Posttransplantation plasmacytic proliferations related to Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:1393–1400. - PubMed
-
- Dotti G., Fiocchi R., Motta T., Facchinetti B., Chiodini B., Borleri G.M., Gavazzeni G., Barbui T., Rambaldi A. Primary effusion lymphoma after heart transplantation: a new entity associated with human herpesvirus-8. Leukemia. 1999;13:664–670. - PubMed
-
- Nador R.G., Cesarman E., Chadburn A., Dawson D.B., Ansari M.Q., Sald J., Knowles D.M. Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood. 1996;88:645–656. - PubMed
-
- Horenstein M.G., Nador R.G., Chadburn A., Hyjek E.M., Inghirami G., Knowles D.M., Cesarman E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in primary effusion lymphomas containing Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8. Blood. 1997;90:1186–1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

