CaMKII-dependent SR Ca leak contributes to doxorubicin-induced impaired Ca handling in isolated cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 21819992
- PMCID: PMC3226826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.07.016
CaMKII-dependent SR Ca leak contributes to doxorubicin-induced impaired Ca handling in isolated cardiac myocytes
Abstract
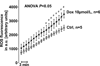
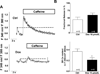
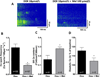
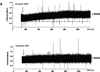
Doxorubicin (DOX) is one of the most effective chemotherapeutic agents, but cardiotoxicity limits DOX therapy. Although the mechanisms are not entirely understood, reactive oxygen species (ROS) appear to be involved in DOX cardiotoxicity. Ca/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) can be activated by ROS through oxidation and is known to contribute to myocardial dysfunction through Ca leakage from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). We hypothesized that CaMKII contributes to DOX-induced defects in intracellular Ca ([Ca](i)) handling. Cardiac myocytes were isolated from wild-type (WT) adult rat hearts and from mouse hearts lacking the predominant myocardial CaMKII isoform (CaMKIIδ(-/-), KO) vs. WT. Isolated cardiomyocytes were investigated 30 min after DOX (10 μmol/L) superfusion, using epifluorescence and confocal microscopy. Intracellular ROS-generation ([ROS](i)) and [Ca](i) handling properties were assessed. In a subset of experiments, KN-93 or AIP (each 1 μmol/L) were used to inhibit CaMKII. Melatonin (Mel, 100 μmol/L) served as ROS-scavenger. Western blots were performed to determine the amount of CaMKII phosphorylation and oxidation. DOX increased [ROS](i) and led to significant diastolic [Ca](i) overload in rat myocytes. This was associated with reduced [Ca](i) transients, a 5.8-fold increased diastolic SR Ca leak and diminished SR Ca content. ROS-scavenging partially rescued Ca handling. Western blots revealed increased CaMKII phosphorylation, but not CaMKII oxidation after DOX. Pharmacological CaMKII inhibition attenuated diastolic [Ca](i) overload after DOX superfusion and led to partially restored [Ca](i) transients and SR Ca content, presumably due to reduced Ca spark frequency. In line with this concept, isoform-specific CaMKIIδ-KO attenuated diastolic [Ca](i) overload and Ca spark frequency. DOX exposure induces CaMKII-dependent SR Ca leakage, which partially contributes to impaired cellular [Ca](i) homeostasis. Pharmacological and genetic CaMKII inhibition attenuated but did not completely abolish the effects of DOX on [Ca](i). In light of the clinical relevance of DOX, further investigations seem appropriate to determine if CaMKII inhibition could reduce DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Yeh ETH, Bickford CL. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: incidence, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:2231–2247. - PubMed
-
- Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L. Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:185–229. - PubMed
-
- Weiss RB. The anthracyclines: will we ever find a better doxorubicin? Semin Oncol. 1992;19:670–686. - PubMed
-
- Zuppinger C, Timolati F, Suter T. Pathophysiology and diagnosis of cancer drug induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovas Toxicol. 2007;7:61–66. - PubMed
-
- Wouters KA, Kremer LC, Miller TL, Herman EH, Lipshultz SE. Protecting against anthracycline-induced myocardial damage: a review of the most promising strategies. Br J Haematol. 2005;131:561–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

