Nocturnin regulates circadian trafficking of dietary lipid in intestinal enterocytes
- PMID: 21820310
- PMCID: PMC3159848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.018
Nocturnin regulates circadian trafficking of dietary lipid in intestinal enterocytes
Abstract
Background: Efficient metabolic function in mammals depends on the circadian clock, which drives temporal regulation of metabolic processes. Nocturnin is a clock-regulated deadenylase that controls its target mRNA expression posttranscriptionally through poly(A) tail removal. Mice lacking nocturnin (Noc(-/-) mice) are resistant to diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis yet are not hyperactive or hypophagic.
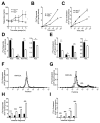
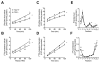
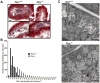
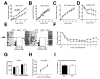
Results: Here we show that nocturnin is expressed rhythmically in the small intestine and is induced by olive oil gavage and that the Noc(-/-) mice have reduced chylomicron transit into the plasma following the ingestion of dietary lipids. Genes involved in triglyceride synthesis and storage and chylomicron formation have altered expression, and large cytoplasmic lipid droplets accumulate in the apical domains of the Noc(-/-) enterocytes. The physiological significance of this deficit in absorption is clear because maintenance of Noc(-/-) mice on diets that challenge the chylomicron synthesis pathway result in significant reductions in body weight, whereas diets that bypass this pathway do not.
Conclusions: Therefore, we propose that nocturnin plays an important role in the trafficking of dietary lipid in the intestinal enterocytes by optimizing efficient absorption of lipids.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Metabolism: what causes the gut's circadian instincts?Curr Biol. 2011 Aug 23;21(16):R624-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.009. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21855001
Similar articles
-
Metabolism: what causes the gut's circadian instincts?Curr Biol. 2011 Aug 23;21(16):R624-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.009. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21855001
-
Loss of Nocturnin, a circadian deadenylase, confers resistance to hepatic steatosis and diet-induced obesity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 5;104(23):9888-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702448104. Epub 2007 May 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17517647 Free PMC article.
-
Nocturnin: at the crossroads of clocks and metabolism.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul;23(7):326-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 May 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22608110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal Control of Metabolic Amplitude by Nocturnin.Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 30;22(5):1225-1235. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.011. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29386110 Free PMC article.
-
Clock regulation of dietary lipid absorption.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012 Jul;15(4):336-41. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283548629. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012. PMID: 22617567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian topology of metabolism.Nature. 2012 Nov 15;491(7424):348-56. doi: 10.1038/nature11704. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23151577 Review.
-
Metabolic and chemical architecture of the mammalian circadian clock.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Sep 21;30(9):1033-1052. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.014. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37708890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-Restricted Eating: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Challenges in Translation.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101161. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101161. Epub 2020 May 15. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32480126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial bioluminescence regulates expression of a host cryptochrome gene in the squid-Vibrio symbiosis.mBio. 2013 Apr 2;4(2):e00167-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00167-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23549919 Free PMC article.
-
Kiss your tail goodbye: the role of PARN, Nocturnin, and Angel deadenylases in mRNA biology.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):571-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23274303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vener KJ, Szabo S, Moore JG. The effect of shift work on gastrointestinal (GI) function: a review. Chronobiologia. 1989;16:421–439. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro DC, Hampton SM, Morgan L, Deacon S, Arendt J. Altered postprandial hormone and metabolic responses in a simulated shift work environment. The Journal of endocrinology. 1998;158:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Baggs JE, Green CB. Nocturnin, a Deadenylase in Xenopus laevis Retina. A Mechanism for Posttranscriptional Control of Circadian-Related mRNA. Curr Biol. 2003;13:189–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

