Elucidating the mechanobiology of malignant brain tumors using a brain matrix-mimetic hyaluronic acid hydrogel platform
- PMID: 21820737
- PMCID: PMC3159794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.005
Elucidating the mechanobiology of malignant brain tumors using a brain matrix-mimetic hyaluronic acid hydrogel platform
Abstract
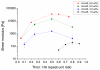
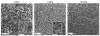
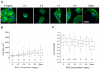
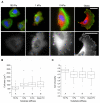
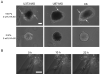
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a malignant brain tumor characterized by diffuse infiltration of single cells into the brain parenchyma, which is a process that relies in part on aberrant biochemical and biophysical interactions between tumor cells and the brain extracellular matrix (ECM). A major obstacle to understanding ECM regulation of GBM invasion is the absence of model matrix systems that recapitulate the distinct composition and physical structure of brain ECM while allowing independent control of adhesive ligand density, mechanics, and microstructure. To address this need, we synthesized brain-mimetic ECMs based on hyaluronic acid (HA) with a range of stiffnesses that encompasses normal and tumorigenic brain tissue and functionalized these materials with short Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides to facilitate cell adhesion. Scanning electron micrographs of the hydrogels revealed a dense, sheet-like microstructure with apparent nanoscale porosity similar to brain extracellular space. On flat hydrogel substrates, glioma cell spreading area and actin stress fiber assembly increased strongly with increasing density of RGD peptide. Increasing HA stiffness under constant RGD density produced similar trends and increased the speed of random motility. In a three-dimensional (3D) spheroid paradigm, glioma cells invaded HA hydrogels with morphological patterns distinct from those observed on flat surfaces or in 3D collagen-based ECMs but highly reminiscent of those seen in brain slices. This material system represents a brain-mimetic model ECM with tunable ligand density and stiffness amenable to investigations of the mechanobiological regulation of brain tumor progression.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492–507. - PubMed
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2683–710. - PubMed
-
- Kunkel P, Ulbricht U, Bohlen P, Brockmann MA, Fillbrandt R, Stavrou D, et al. Inhibition of glioma angiogenesis and growth in vivo by systemic treatment with a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res. 2001;61(18):6624–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

