Development of thymic NK cells from double negative 1 thymocyte precursors
- PMID: 21821702
- PMCID: PMC3186333
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-359679
Development of thymic NK cells from double negative 1 thymocyte precursors
Abstract
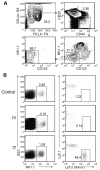
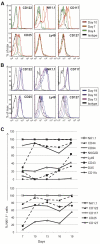
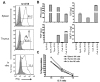
The differentiation of natural killer (NK) cells and a subpopulation of NK cells which requires an intact thymus, that is, thymic NK cells, is poorly understood. Previous in vitro studies indicate that double negative (CD4⁻CD8⁻, DN) thymocytes can develop into cells with NK cell markers, but these cells have not been well characterized. Herein, we generated and characterized NK cells differentiating from thymic DN precursors. Sorted DN1 (CD44⁺CD25⁻) CD122⁻NK1.1⁻ thymocytes from Rag1(⁻/⁻) mice were adoptively transferred into Rag1(⁻/⁻)Ly5.1 congenic mice. After intrathymic injection, donor-derived cells phenotypically resembling thymic NK cells were found. To further study their differentiation, we seeded sorted DN1 CD122⁻)NK1.1⁻ thymocytes on irradiated OP9 bone marrow stromal cells with IL-15, IL-7, Flt3L, and stem cell factor. NK1.1⁺ cells emerged after 7 days. In vitro differentiated NK cells acquired markers associated with immature bone marrow-derived NK cells, but also expressed CD127, which is typically found on thymic NK cells. Furthermore, we found that in vitro cells generated from thymic precursors secreted cytokines when stimulated and degranulated on target exposure. Together, these data indicate that functional thymic NK cells can develop from a DN1 progenitor cell population.
Figures



References
-
- Yokoyama WM. Chapter 17, Natural killer cells. In: Paul WE, editor. Fundamental Immunology. New York, NY: Lippincott-Raven; 2008. pp. 483–517.
-
- Yokoyama WM, Kim S, French AR. The dynamic life of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:405–429. - PubMed
-
- Di Santo JP. Natural killer cell developmental pathways: a question of balance. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:257–286. - PubMed
-
- Igarashi H, Gregory SC, Yokota T, Sakaguchi N, Kincade PW. Transcription from the RAG1 locus marks the earliest lymphocyte progenitors in bone marrow. Immunity. 2002;17(2):117–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

