Binding of activating transcription factor 6 to the A5/Core of the rat insulin II gene promoter does not mediate its transcriptional repression
- PMID: 21821716
- PMCID: PMC3185209
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-11-0016
Binding of activating transcription factor 6 to the A5/Core of the rat insulin II gene promoter does not mediate its transcriptional repression
Abstract
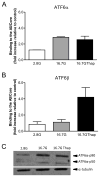
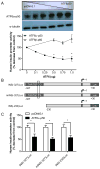
Pancreatic β-cells have a well-developed endoplasmic reticulum due to their highly specialized secretory function to produce insulin in response to glucose and nutrients. It has been previously reported that overexpression of activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) reduces insulin gene expression in part via upregulation of small heterodimer partner. In this study, we investigated whether ATF6 directly binds to the insulin gene promoter, and whether its direct binding represses insulin gene promoter activity. A bioinformatics analysis identified a putative ATF6 binding site in the A5/Core region of the rat insulin II gene promoter. Direct binding of ATF6 was confirmed using several approaches. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays in nuclear extracts from MCF7 cells, isolated rat islets and insulin-secreting HIT-T15 cells showed ATF6 binding to the native A5/Core of the rat insulin II gene promoter. Antibody-mediated supershift analyses revealed the presence of both ATF6 isoforms, ATF6α and ATF6β, in the complex. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed the binding of ATF6α and ATF6β to a region encompassing the A5/Core of the rat insulin II gene promoter in isolated rat islets. Overexpression of the active (cleaved) fragment of ATF6α, but not ATF6β, inhibited the activity of an insulin promoter-reporter by 50%. However, the inhibitory effect of ATF6α was insensitive to mutational inactivation or deletion of the A5/Core. Therefore, although ATF6 binds directly to the A5/Core of the rat insulin II gene promoter, this direct binding does not appear to contribute to its repressive activity.
© 2011 Society for Endocrinology
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Allagnat F, Christulia F, Ortis F, Pirot P, Lortz S, Lenzen S, et al. Sustained production of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces pancreatic beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Diabetologia. 2010;53(6):1120–1130. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti SK, James JC, Mirmira RG. Quantitative assessment of gene targeting in vitro and in vivo by the pancreatic transcription factor, Pdx1. Importance of chromatin structure in directing promoter binding. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(15):13286–13293. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Shen J, Prywes R. The luminal domain of ATF6 senses endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and causes translocation of ATF6 from the ER to the Golgi. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(15):13045–13052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

