Overcoming fluctuation and leakage problems in the quantification of intracellular 2-oxoglutarate levels in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 21821754
- PMCID: PMC3187092
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05257-11
Overcoming fluctuation and leakage problems in the quantification of intracellular 2-oxoglutarate levels in Escherichia coli
Abstract
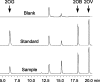
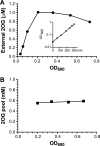
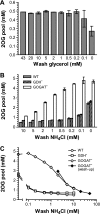
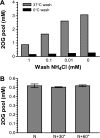
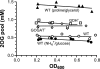
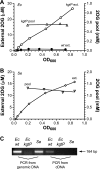
2-Oxoglutarate is located at the junction between central carbon and nitrogen metabolism, serving as an intermediate for both. In nitrogen metabolism, 2-oxoglutarate acts as both a carbon skeletal carrier and an effector molecule. There have been only sporadic reports of its internal concentrations. Here we describe a sensitive and accurate method for determination of the 2-oxoglutarate pool concentration in Escherichia coli. The detection was based on fluorescence derivatization followed by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography separation. Two alternative cell sampling strategies, both of which were based on a fast filtration protocol, were sequentially developed to overcome both its fast metabolism and contamination from 2-oxoglutarate that leaks into the medium. We observed rapid changes in the 2-oxoglutarate pool concentration upon sudden depletion of nutrients: decreasing upon carbon depletion and increasing upon nitrogen depletion. The latter was studied in mutants lacking either of the two enzymes using 2-oxoglutarate as the carbon substrate for glutamate biosynthesis. The results suggest that flux restriction on either reaction greatly influences the internal 2-oxoglutarate level. Additional study indicates that KgtP, a 2-oxoglutarate proton symporter, functions to recover the leakage loss of 2-oxoglutarate. This recovery mechanism benefits the measurement of cellular 2-oxoglutarate level in practice by limiting contamination from 2-oxoglutarate leakage.
Figures
References
-
- Alibhai M., Villafranca J. J. 1994. Kinetic and mutagenic studies of the role of the active site residues Asp-50 and Glu-327 of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry 33:682–686 - PubMed
-
- Bolten C. J., Kiefer P., Letisse F., Portais J. C., Wittmann C. 2007. Sampling for metabolome analysis of microorganisms. Anal. Chem. 79:3843–3849 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

