Persistence of antibiotic resistance: evaluation of a probiotic approach using antibiotic-sensitive Megasphaera elsdenii strains to prevent colonization of swine by antibiotic-resistant strains
- PMID: 21821757
- PMCID: PMC3194883
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00647-11
Persistence of antibiotic resistance: evaluation of a probiotic approach using antibiotic-sensitive Megasphaera elsdenii strains to prevent colonization of swine by antibiotic-resistant strains
Abstract
Megasphaera elsdenii is a lactate-fermenting, obligately anaerobic bacterium commonly present in the gastrointestinal tracts of mammals, including humans. Swine M. elsdenii strains were previously shown to have high levels of tetracycline resistance (MIC=64 to >256 μg/ml) and to carry mosaic (recombinant) tetracycline resistance genes. Baby pigs inherit intestinal microbiota from the mother sow. In these investigations we addressed two questions. When do M. elsdenii strains from the sow colonize baby pigs? Can five antibiotic-sensitive M. elsdenii strains administered intragastrically to newborn pigs affect natural colonization of the piglets by antibiotic-resistant (AR) M. elsdenii strains from the mother? M. elsdenii natural colonization of newborn pigs was undetectable (<10(4) CFU/g [wet weight] of feces) prior to weaning (20 days after birth). After weaning, all pigs became colonized (4 × 10(5) to 2 × 10(8) CFU/g feces). In a separate study, 61% (76/125) of M. elsdenii isolates from a gravid sow never exposed to antibiotics were resistant to chlortetracycline, ampicillin, or tylosin. The inoculation of the sow's offspring with mixtures of M. elsdenii antibiotic-sensitive strains prevented colonization of the offspring by maternal AR strains until at least 11 days postweaning. At 25 and 53 days postweaning, however, AR strains predominated. Antibiotic susceptibility phenotypes and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based identities of M. elsdenii isolated from sow and offspring were unexpectedly diverse. These results suggest that dosing newborn piglets with M. elsdenii antibiotic-sensitive strains delays but does not prevent colonization by maternal resistant strains. M. elsdenii subspecies diversity offers an explanation for the persistence of resistant strains in the absence of antibiotic selection.
Figures
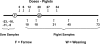
Similar articles
-
Isolation of tetracycline-resistant Megasphaera elsdenii strains with novel mosaic gene combinations of tet(O) and tet(W) from swine.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jul;69(7):3874-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.7.3874-3882.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12839756 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse tetracycline resistance genotypes of Megasphaera elsdenii strains selectively cultured from swine feces.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jun;70(6):3754-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3754-3757.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184185 Free PMC article.
-
Chlortetracycline-resistant intestinal bacteria in organically raised and feral Swine.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Oct;77(20):7167-70. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00688-11. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21821750 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Maternal Probiotic or Synbiotic Supplementation on Sow and Offspring Gastrointestinal Microbiota, Health, and Performance.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;13(19):2996. doi: 10.3390/ani13192996. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of Escherichia coli O157 strains from humans, cattle and pigs in the North-West Province, South Africa.Int J Food Microbiol. 2008 Dec 10;128(2):181-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.08.011. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Int J Food Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18848733 Review.
Cited by
-
Butyrate-producing bacteria, including mucin degraders, from the swine intestinal tract.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jun;79(12):3879-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00589-13. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23584773 Free PMC article.
-
Use of biotics in animals: impact on nutrition, health, and food production.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf061. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf061. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40036559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Inoculation of Microbial Suspension in Suckling Piglets Affects the Transmission of Maternal Microbiota and the Associated Antibiotic Resistance Genes.Microorganisms. 2020 Oct 13;8(10):1576. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101576. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33066283 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Diversity and Biochemical Analysis of Suanzhou: A Traditional Chinese Fermented Cereal Gruel.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 25;7:1311. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01311. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27610102 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance: how much do we know and where do we go from here?Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Oct;77(20):7093-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06565-11. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21908629 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Contreras A., Maxwell A. 1992. gyrB mutations which confer coumarin resistance also affect DNA supercoiling and ATP hydrolysis by Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Mol. Microbiol. 6:1617–1624 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

