Unifying ideas for non-parametric linkage analysis
- PMID: 21822022
- PMCID: PMC7077094
- DOI: 10.1159/000323752
Unifying ideas for non-parametric linkage analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Non-parametric linkage analysis (NPL) exploits marker allele sharing among affected relatives to map genes influencing complex traits. Computational barriers force approximate analysis on large pedigrees and the adoption of a questionable perfect data assumption (PDA) in assigning p values. To improve NPL significance testing on large pedigrees, we examine the adverse consequences of missing data and PDA. We also introduce a novel statistic, Q-NPL, appropriate for NPL analysis of quantitative traits.
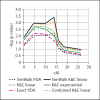
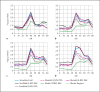
Methods: Using simulated and real data sets with qualitative traits, we compare NPL analysis results for four testing procedures and various degrees of missing data. The simulated data sets vary from all nuclear families, to all large pedigrees, to a mix of pedigrees of different sizes. We implemented the Kong and Cox linear adjustment of p values in the software packages Mendel and SimWalk. We perform similar analysis with Q-NPL on quantitative traits of various heritabilities.
Results: The Kong and Cox extension for significance testing is robust to realistic missing data patterns, greatly improves p values in approximate analyses, and works equally well for qualitative and quantitative traits and small and large pedigrees. The Q-NPL statistic is robust to missing data and shows good power to detect linkage for quantitative traits with a wide spectrum of heritabilities.
Conclusions: The Kong and Cox extension should be a standard tool for calculating NPL p values. It allows the combination of exact and estimated analyses into a single significance score. Q-NPL should be a standard statistic for NPL analysis of quantitative traits. The new statistics are implemented in Mendel and SimWalk.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures








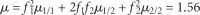

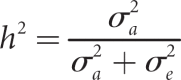

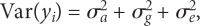





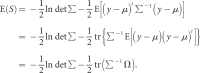


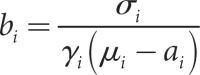

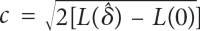


Similar articles
-
A study comparing precision of the maximum multipoint heterogeneity LOD statistic to three model-free multipoint linkage methods.Genet Epidemiol. 2001 Dec;21(4):315-25. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1037. Genet Epidemiol. 2001. PMID: 11754467
-
Statistics for nonparametric linkage analysis of X-linked traits in general pedigrees.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Jan;70(1):181-91. doi: 10.1086/338308. Epub 2001 Nov 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11719901 Free PMC article.
-
Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach.Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1347-63. Am J Hum Genet. 1996. PMID: 8651312 Free PMC article.
-
How to model a complex trait. 1. General considerations and suggestions.Hum Hered. 2003;55(4):202-10. doi: 10.1159/000073204. Hum Hered. 2003. PMID: 14566098 Review.
-
Gene finding strategies.Biol Psychol. 2002 Oct;61(1-2):53-71. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0511(02)00052-2. Biol Psychol. 2002. PMID: 12385669 Review.
References
-
- Altshuler D, Daly M. Guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. Nature Genet. 2007;39:813–815. - PubMed
-
- Whittemore A, Halpern J. A class of tests for linkage using affected pedigree members. Biometrics. 1994;50:118–127. - PubMed
-
- Whittemore A, Halpern J. Probability of gene identity by descent: computation and applications. Biometrics. 1994;50:109–117. - PubMed
-
- Abecasis G, et al. Merlin − rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

