An infrared fluorescent protein for deeper imaging
- PMID: 21822247
- PMCID: PMC5734861
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1941
An infrared fluorescent protein for deeper imaging
Abstract
A newly engineered infrared fluorescent protein will allow microscopists to peer more deeply into living animals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
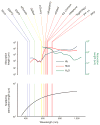
Comment on
-
Bright and stable near-infrared fluorescent protein for in vivo imaging.Nat Biotechnol. 2011 Jul 17;29(8):757-61. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1918. Nat Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21765402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

