The inducible kinase IKKi is required for IL-17-dependent signaling associated with neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation
- PMID: 21822257
- PMCID: PMC3282992
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2080
The inducible kinase IKKi is required for IL-17-dependent signaling associated with neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation
Abstract
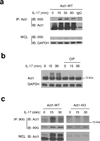
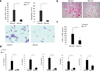
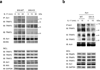
Interleukin 17 (IL-17) is critical in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Here we report that Act1, the key adaptor for the IL-17 receptor (IL-7R), formed a complex with the inducible kinase IKKi after stimulation with IL-17. Through the use of IKKi-deficient mice, we found that IKKi was required for IL-17-induced expression of genes encoding inflammatory molecules in primary airway epithelial cells, neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation. IKKi deficiency abolished IL-17-induced formation of the complex of Act1 and the adaptors TRAF2 and TRAF5, activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and mRNA stability, whereas the Act1-TRAF6-transcription factor NF-κB axis was retained. IKKi was required for IL-17-induced phosphorylation of Act1 on Ser311, adjacent to a putative TRAF-binding motif. Substitution of the serine at position 311 with alanine impaired the IL-17-mediated Act1-TRAF2-TRAF5 interaction and gene expression. Thus, IKKi is a kinase newly identified as modulating IL-17 signaling through its effect on Act1 phosphorylation and consequent function.
Figures









Comment in
-
IL-17R signaling: new players get in on the Act1.Nat Immunol. 2011 Aug 18;12(9):813-5. doi: 10.1038/ni.2093. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21852777 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bettelli E, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

