RALA and RALBP1 regulate mitochondrial fission at mitosis
- PMID: 21822277
- PMCID: PMC3167028
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2310
RALA and RALBP1 regulate mitochondrial fission at mitosis
Abstract
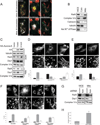
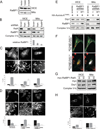
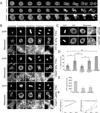
Mitochondria exist as dynamic interconnected networks that are maintained through a balance of fusion and fission. Equal distribution of mitochondria to daughter cells during mitosis requires fission. Mitotic mitochondrial fission depends on both the relocalization of the large GTPase DRP1 to the outer mitochondrial membrane and phosphorylation of Ser 616 on DRP1 by the mitotic kinase cyclin B-CDK1 (ref. 2). We now report that these processes are mediated by the small Ras-like GTPase RALA and its effector RALBP1 (also known as RLIP76, RLIP1 or RIP1; refs 3, 4). Specifically, the mitotic kinase Aurora A phosphorylates Ser 194 of RALA, relocalizing it to the mitochondria, where it concentrates RALBP1 and DRP1. Furthermore, RALBP1 is associated with cyclin B-CDK1 kinase activity that leads to phosphorylation of DRP1 on Ser 616. Disrupting either RALA or RALBP1 leads to a loss of mitochondrial fission at mitosis, improper segregation of mitochondria during cytokinesis and a decrease in ATP levels and cell number. Thus, the two mitotic kinases Aurora A and cyclin B-CDK1 converge on RALA and RALBP1 to promote mitochondrial fission, the appropriate distribution of mitochondria to daughter cells and ultimately proper mitochondrial function.
Figures


Comment in
-
Coupling mitochondrial and cell division.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Sep 2;13(9):1026-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb2334. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21892144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Detmer SA, Chan DC. Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:870–879. - PubMed
-
- Taguchi N, Ishihara N, Jofuku A, Oka T, Mihara K. Mitotic phosphorylation of dynamin-related GTPase Drp1 participates in mitochondrial fission. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:11521–11529. - PubMed
-
- Camonis JH, White MA. Ral GTPases: corrupting the exocyst in cancer cells. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:327–332. - PubMed
-
- Feig LA. Ral-GTPases: approaching their 15 minutes of fame. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:419–425. - PubMed
-
- Wu JC, et al. Identification of V23RalA-Ser194 as a critical mediator for Aurora-A-induced cellular motility and transformation by small pool expression screening. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:9013–9022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

