Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2
- PMID: 21822285
- PMCID: PMC3888478
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2416
Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2
Abstract
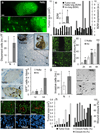
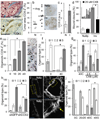
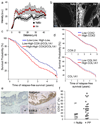
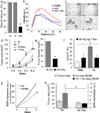
The prognosis of breast cancer in young women is influenced by reproductive history. Women diagnosed within 5 years postpartum have worse prognosis than nulliparous women or women diagnosed during pregnancy. Here we describe a mouse model of postpartum breast cancer that identifies mammary gland involution as a driving force of tumor progression. In this model, human breast cancer cells exposed to the involuting mammary microenvironment form large tumors that are characterized by abundant fibrillar collagen, high cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and an invasive phenotype. In culture, tumor cells are invasive in a fibrillar collagen and COX-2-dependent manner. In the involuting mammary gland, inhibition of COX-2 reduces the collagen fibrillogenesis associated with involution, as well as tumor growth and tumor cell infiltration to the lung. These data support further research to determine whether women at high risk for postpartum breast cancer would benefit from treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) during postpartum involution.
Figures


References
-
- Lambe M, et al. Transient increase in the risk of breast cancer after giving birth. The New England journal of medicine. 1994;331:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Mathews TJ, Hamilton BE. Delayed Childbearing: More Women Are Having Their First Child Later in Life. Vol. 21. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2009.
-
- Daling JR, Malone KE, Doody DR, Anderson BO, Porter PL. The relation of reproductive factors to mortality from breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002;11:235–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

