Radiolabeled oligonucleotides for antisense imaging
- PMID: 21822406
- PMCID: PMC3148791
- DOI: 10.2174/157017911796117241
Radiolabeled oligonucleotides for antisense imaging
Abstract
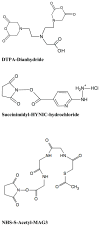
Oligonucleotides radiolabeled with isotopes emitting γ-rays (for SPECT imaging) or positrons (for PET imaging) can be useful for targeting messenger RNA (mRNA) thereby serving as non-invasive imaging tools for detection of gene expression in vivo (antisense imaging). Radiolabeled oligonucleotides may also be used for monitoring their in vivo fate, thereby helping us better understand the barriers to its delivery for antisense targeting. These developments have led to a new area of molecular imaging and targeting, utilizing radiolabeled antisense oligonucleotides. However, the success of antisense imaging relies heavily on overcoming the barriers for its targeted delivery in vivo. Furthermore, the low ability of the radiolabeled antisense oligonucleotide to subsequently internalize into the cell and hybridize with its target mRNA poses additional challenges in realizing its potentials. This review covers the advances in the antisense imaging probe development for PET and SPECT, with an emphasis on radiolabeling strategies, stability, delivery and in vivo targeting.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular imaging of MDM2 messenger RNA with 99mTc-labeled antisense oligonucleotides in experimental human breast cancer xenografts.J Nucl Med. 2010 Nov;51(11):1805-12. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.077982. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20956468
-
The effect of Tc-99m-labeled MDM2 antisense oligonucleotide on gene expression in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.J Exp Ther Oncol. 2007;6(4):297-303. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2007. PMID: 18038763
-
Uptake kinetics of 99mTc-MAG3-antisense oligonucleotide to PCNA and effect on gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Nucl Med. 2005 Jun;46(6):1052-8. J Nucl Med. 2005. PMID: 15937319
-
99mTc-N,N'-Bis(S-benzoyl-thioglycoloyl)diamidopropanoyl-KRAS-PNA-d(Cys-Ser-Lys-Cys).2007 Aug 9 [updated 2008 Jan 3]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2007 Aug 9 [updated 2008 Jan 3]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641936 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
99mTc-Hydrazinonicotinamide/tricine-eighteen-nucleotide RIα mRNA antisense small interfering oligoribonucleotides.2007 Sep 21 [updated 2007 Oct 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2007 Sep 21 [updated 2007 Oct 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641255 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear imaging of liposomal drug delivery systems: A critical review of radiolabelling methods and applications in nanomedicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Mar 15;143:134-160. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.05.012. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019. PMID: 31170428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trans-Cyclooctene Isomerization Catalyzed by Thiamine Degradation Products in Cell Culture Media.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 5;10(23):24768-24777. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01780. eCollection 2025 Jun 17. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40547704 Free PMC article.
-
Rationale for MYC imaging and targeting in pancreatic cancer.EJNMMI Res. 2021 Oct 12;11(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13550-021-00843-1. EJNMMI Res. 2021. PMID: 34637026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tumor multicomponent targeting chemoimmune drug delivery system for reprograming the tumor microenvironment and personalized cancer therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2018 Jul;23(7):1344-1356. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Drug Discov Today. 2018. PMID: 29551455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Organometallic Oligonucleotides through Oximation with Metalated Benzaldehydes.ACS Omega. 2019 Nov 1;4(20):18803-18808. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02804. eCollection 2019 Nov 12. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31737842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nielsen P. Targeting double stranded DNA with peptide nucleic acid (PNA) Curr Med Chem. 2001;8(5):545–550. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn H, Demidov V, Nielsen P, Frank-Kamenetskii M. An experimental study of mechanism and specificity of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) binding to duplex DNA. J Mol Biol. 1999;286(5):1337–1345. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal S, Zhao Q. Antisense therapeutics. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998;2(4):519–528. - PubMed
-
- Monteith D, Levin A. Synthetic oligonucleotides: the development of antisense therapeutics. Toxicol Pathol. 1999;27(1):8–13. - PubMed
-
- Gambhir S. Molecular imaging of cancer with positron emission tomography. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(9):683–693. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
