Digestive enzymes of the crustaceans Munida and their application in cheese manufacturing: a review
- PMID: 21822412
- PMCID: PMC3148499
- DOI: 10.3390/md9071220
Digestive enzymes of the crustaceans Munida and their application in cheese manufacturing: a review
Abstract
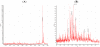
Crustaceans Munida (fam. Galatheideae, ord. Decapodi) were fished in the Southern Adriatic Sea and their proteolytic activities were characterized and tested for potential application in cheese manufacturing. Enzymes extracted from whole crustaceans, mainly serine proteases, showed high caseinolytic and moderate clotting activities. Analysis by 2D zymography of the digestive enzymes extracted from Munida hepatopancreas, showed the presence of several isotrypsin- and isochymotrypsin-like enzymes in the range of 20-34 kDa and 4.1-5.8 pI. Moreover, specific enzymatic assays showed the presence of aminopeptidases and carboxypeptidases A and B. Overall, optimum activity was achieved at pH 7.5 and 40-45 °C. Caseinolytic activity, determined both spectrophotometrically and by SDS gel electrophoresis, indicated higher activity on β-casein than on α-casein. Miniature cheddar-type cheeses and Pecorino-type cheeses were manufactured by adding starter, rennet and Munida extracts to milk. Reverse-phase HPLC and MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry showed a more complex pattern of proteolytic products in cheeses made using Munida instead of chymosin. Munida extracts were found to degrade the chymosin-derived β-casein fragment f193-209, one of the peptides associated with bitterness in cheese. In conclusion, Munida digestive enzymes represent a promising tool for development of new cheese products and shorten cheese ripening when used either alone or in addition to calf rennet.
Keywords: cheese; crustaceans; enzymes; proteases.
Figures


References
-
- Rasmussen RS, Morrissey MT. Marine biotechnology for production of food ingredients. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2007;52:237–292. - PubMed
-
- Debashish G, Malay S, Barindra S, Joydeep M. Marine enzymes. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2005;96:189–218. - PubMed
-
- Haefner B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today. 2003;8:536–544. - PubMed
-
- Bernan VS, Greenstein M, Maiese WM. Marine micro-organisms as a source of new natural products. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1997;43:57–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

