Role of JNK-1 regulation in the protection of contact-inhibited fibroblasts from oxidative stress
- PMID: 21822690
- PMCID: PMC3219803
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-011-1004-1
Role of JNK-1 regulation in the protection of contact-inhibited fibroblasts from oxidative stress
Abstract
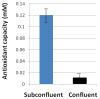
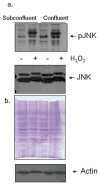
The molecular signaling events leading to protection from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis upon contact inhibition have not been fully investigated. Previous research has indicated a role for mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in the regulation of contact inhibition, and these proteins have also been associated with cell cycle regulation and stress-induced apoptosis. The potential role of the MAPK JNK-1 in the stress-response of actively proliferating and contact-inhibited cells was investigated. Actively proliferating normal fibroblasts (BJ) and fibrosarcoma cells (HT-1080) were stressed with H2O2, and levels of activated JNK-1 and cleaved PARP were ascertained. Similarly, these results were compared with levels of activated JNK-1 and cleaved PARP detected in H2O2-stressed confluent fibrosarcoma or contact-inhibited fibroblast cells. Contact-inhibited fibroblasts were protected from apoptosis in comparison to subconfluent fibroblasts, concurrent with decreased JNK-1 activation. Increased culture density of fibrosarcoma cells was not protective against apoptosis, and these cells did not demonstrate density-dependent alterations in the JNK-1 stress response. This decreased activation of JNK-1 in stressed, contact-inhibited cells did not appear to be dependent upon increased expression of MKP-1; however, over-expression of MKP-1 was sufficient to result in a slight decrease in H2O2-stimulated PARP cleavage. Increasing the antioxidant capacity of fibroblasts through NAC-treatment not only lessened H2O2-stimulated JNK-1 activation, but also did not influence the expression of MKP-1. Taken together, these results suggest that regulation of negative regulation of JNK-1 upon contact inhibition is protective against apoptosis, and that this regulation is independent of MKP-1.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Regulation of MKP-1 expression and MAPK activation by PARP-1 in oxidative stress: a new mechanism for the cytoplasmic effect of PARP-1 activation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Dec 15;49(12):1978-88. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.026. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20920579
-
Attenuation of p38 MAPK activity upon contact inhibition in fibroblasts.Mol Cell Biochem. 2008 Jan;308(1-2):65-73. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9613-4. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17906919
-
ERK regulation upon contact inhibition in fibroblasts.Mol Cell Biochem. 2006 Jun;286(1-2):181-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-9089-z. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16467968
-
Mediation by arachidonic acid metabolites of the H2O2-induced stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase).Eur J Biochem. 1997 Mar 1;244(2):587-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00587.x. Eur J Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9119028
-
The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in oxidative damage-induced cell death.Cancer Res. 2006 May 1;66(9):4888-94. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4229. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16651445
Cited by
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) modulates oligodendrocyte progenitor cell architecture, proliferation and myelination.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86673-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790350 Free PMC article.
-
Kumquat essential oil decreases proliferation and activates JNK signaling and apoptosis in HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Feb;477(2):445-453. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04291-2. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34783965
-
Manuka Essential Oil Triggers Apoptosis and Activation of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in Fibroblasts and Fibrosarcoma Cells.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5168. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215168. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519810 Free PMC article.
-
Density-dependent ERK MAPK expression regulates MMP-9 and influences growth.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;456(1-2):115-122. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03496-w. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30689107 Free PMC article.
-
Rosavin extends lifespan via the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;397(7):5275-5287. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-02952-9. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38277040
References
-
- Robinson MJ, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Bio. 1997;9:180–186. - PubMed
-
- Pelech SL. Networking with protein kinases. Curr Biol. 1993;3:513–515. - PubMed
-
- Slack DN, Seternes OM, Gabrielsen M, Keyse SM. Distinct binding determinants forERK2/p38α and JNK MAP kinases mediate catalytic activation and substrate selectivity of MAP kinase phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16491–16500. - PubMed
-
- Keshet Y, Seger R. The MAP kinase signaling cascades: a system of hundreds of components regulates a diverse array of physiological functions. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;661:3–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

