Profiling and quantitative evaluation of three nickel-coated magnetic matrices for purification of recombinant proteins: helpful hints for the optimized nanomagnetisable matrix preparation
- PMID: 21824404
- PMCID: PMC3163181
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-31
Profiling and quantitative evaluation of three nickel-coated magnetic matrices for purification of recombinant proteins: helpful hints for the optimized nanomagnetisable matrix preparation
Abstract
Background: Several materials are available in the market that work on the principle of protein magnetic fishing by their histidine (His) tags. Little information is available on their performance and it is often quoted that greatly improved purification of histidine-tagged proteins from crude extracts could be achieved. While some commercial magnetic matrices could be used successfully for purification of several His-tagged proteins, there are some which have been proved to operate just for a few extent of His-tagged proteins. Here, we address quantitative evaluation of three commercially available Nickel nanomagnetic beads for purification of two His-tagged proteins expressed in Escherichia coli and present helpful hints for optimized purification of such proteins and preparation of nanomagnetisable matrices.
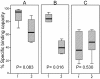
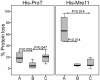
Results: Marked differences in the performance of nanomagnetic matrices, principally on the basis of their specific binding capacity, recovery profile, the amount of imidazole needed for protein elution and the extent of target protein loss and purity were obtained. Based on the aforesaid criteria, one of these materials featured the best purification results (SiMAG/N-NTA/Nickel) for both proteins at the concentration of 4 mg/ml, while the other two (SiMAC-Nickel and SiMAG/CS-NTA/Nickel) did not work well with respect to specific binding capacity and recovery profile.
Conclusions: Taken together, functionality of different types of nanomagnetic matrices vary considerably. This variability may not only be dependent upon the structure and surface chemistry of the matrix which in turn determine the affinity of interaction, but, is also influenced to a lesser extent by the physical properties of the protein itself. Although the results of the present study may not be fully applied for all nanomagnetic matrices, but provide a framework which could be used to profiling and quantitative evaluation of other magnetisable matrices and also provide helpful hints for those researchers facing same challenge.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel nickel-modified nano-magnetite for isolation of histidine-tagged proteins expressed in Escherichia coli.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Nov;413(27):6813-6821. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03637-5. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34491395
-
Super magnetic nanoparticles NiFe2O4, coated with aluminum-nickel oxide sol-gel lattices to safe, sensitive and selective purification of his-tagged proteins.Protein Expr Purif. 2016 May;121:52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Protein Expr Purif. 2016. PMID: 26792558
-
Ni-modified magnetic nanoparticles for affinity purification of His-tagged proteins from the complex matrix of the silkworm fat body.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Nov 6;18(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00715-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 33158450 Free PMC article.
-
Selective binding, magnetic separation and purification of histidine-tagged protein using biopolymer magnetic core-shell nanoparticles.Protein Expr Purif. 2018 Apr;144:5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Protein Expr Purif. 2018. PMID: 29154996
-
Novel purification system for 6xHis-tagged proteins by magnetic affinity separation.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003 Aug 15;793(2):325-9. doi: 10.1016/s1570-0232(03)00332-5. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12906907
Cited by
-
Generation of anti-SN38 antibody for loading efficacy and therapeutic monitoring of SN38-containing therapeutics.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 18;10(12):e33232. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33232. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39021912 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated pharmaceutical protein development with integrated cell free expression, purification, and bioconjugation.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 10;8(1):11967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30435-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30097621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hochuli E, Bannwarth W, Doebeli H, Gentz R, Stueber D. Genetic Approach to Facilitate Purification of Recombinant Proteins with a Novel Metal Chelate adsorbent. BioTechnology. 1988. pp. 1321–1325.
-
- Hochuli E, Doebeli H, Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1987;411:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Gaber-Porekar V, Menart V. Potential for using histidine tags in purification of proteins at large scale. chemical engineering technology. 2005;28:1306–1314. doi: 10.1002/ceat.200500167. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

