Anterograde or retrograde transsynaptic labeling of CNS neurons with vesicular stomatitis virus vectors
- PMID: 21825165
- PMCID: PMC3174680
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110854108
Anterograde or retrograde transsynaptic labeling of CNS neurons with vesicular stomatitis virus vectors
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 5;109(23):9219
Abstract
To understand how the nervous system processes information, a map of the connections among neurons would be of great benefit. Here we describe the use of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) for tracing neuronal connections in vivo. We made VSV vectors that used glycoprotein (G) genes from several other viruses. The G protein from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus endowed VSV with the ability to spread transsynaptically, specifically in an anterograde direction, whereas the rabies virus glycoprotein gave a specifically retrograde transsynaptic pattern. The use of an avian G protein fusion allowed specific targeting of cells expressing an avian receptor, which allowed a demonstration of monosynaptic anterograde tracing from defined cells. Synaptic connectivity of pairs of virally labeled cells was demonstrated by using slice cultures and electrophysiology. In vivo infections of several areas in the mouse brain led to the predicted patterns of spread for anterograde or retrograde tracers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
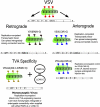
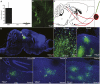
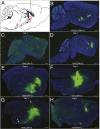
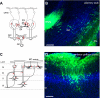
Comment in
-
Neural circuits look forward.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 27;108(39):16137-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112842108. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21914847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Enquist L-W, Card J-P. Recent advances in the use of neurotropic viruses for circuit analysis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:603–606. - PubMed
-
- Kelly R-M, Strick P-L. Rabies as a transneuronal tracer of circuits in the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods. 2000;103:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Enquist L-W. Exploiting circuit-specific spread of pseudorabies virus in the central nervous system: Insights to pathogenesis and circuit tracers. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(Suppl 2):S209–S214. - PubMed
-
- Sun X, Belouzard S, Whittaker G-R. Molecular architecture of the bipartite fusion loops of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G, a class III viral fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:6418–6427. - PubMed
-
- Mebatsion T, Konig M, Conzelmann K-K. Budding of rabies virus particles in the absence of the spike glycoprotein. Cell. 1996;84:941–951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

