Macrophage polarization in metabolic disorders: functions and regulation
- PMID: 21825981
- PMCID: PMC3565956
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32834a77b4
Macrophage polarization in metabolic disorders: functions and regulation
Abstract
Purpose of review: To discuss recent findings on the role and regulation of macrophage polarization in obesity and atherosclerosis.
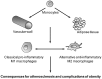
Recent findings: Macrophages infiltrate the vascular wall during atherosclerosis and adipose tissue during obesity. At least two distinct subpopulations with different functions, the classically (M1) and the alternatively (M2) activated macrophages, have been found in these tissues. Reciprocal skewing of macrophage polarization between the M1 and M2 states is a process modulated by diet, humoral and transcription factors, such as the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Summary: Recent literature highlights the importance not only of the number of infiltrated macrophages, but also their activation in the maintenance of the inflammation state. Identifying mechanisms and molecules able to modify the balance between M1 and M2 represents a promising field of research.
Figures

References
-
- Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Ancuta P, Crowe S, et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood. 2010;116:e74–80. - PubMed
-
- Geissmann F, Jung S, Littman DR. Blood monocytes consist of two principal subsets with distinct migratory properties. Immunity. 2003;19:71–82. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:677–86. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CF, Gerber JS, Mosser DM. Modulating macrophage function with IgG immune complexes. J Endotoxin Res. 2002;8:477–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

