Barriers to antiretroviral initiation in HIV-1-discordant couples
- PMID: 21826010
- PMCID: PMC3202340
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31822f064e
Barriers to antiretroviral initiation in HIV-1-discordant couples
Abstract
Background: In Kenya and much of sub-Saharan Africa, nearly half of all couples affected by HIV are discordant. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) slows disease progression in HIV-1-infected individuals and reduces transmission to uninfected partners. We examined time to ART initiation and factors associated with delayed initiation in HIV-1-discordant couples in Nairobi.
Methods: HIV-1-discordant couples were enrolled and followed quarterly for up to 2 years. Clinical staff administered questionnaires and conducted viral loads and CD4 counts. Participants with a CD4 count meeting ART criteria were referred to a nearby US President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief-funded treatment center. Barriers to ART initiation among participants with a CD4 count eligible for ART were assessed by Cox regression.
Results: Of 439 HIV-1-infected participants (63.6% females and 36.4% males), 146 met CD4 count criteria for ART during follow-up. Median time from meeting CD4 criteria until ART initiation was 8.9 months, with 42.0% of eligible participants on ART by 6 months and 63.4% on ART by 1 year. The CD4 count at the time of eligibility was inversely associated with time to ART initiation (hazard ratio = 0.49, P < 0.001). Compared with homeowners, those paying higher rents started ART 48% more slowly (P = 0.062) and those paying lower rents started 71% more slowly (P = 0.002).
Conclusions: Despite access to regular health care, referrals to treatment centers, and free access to ART, over one-third of participants with an eligible CD4 count had not started ART within 1 year. Factors of lower socioeconomic status may slow ART initiation, and targeted approaches are needed to avoid delays in treatment initiation.
Figures
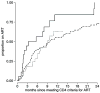
 ] those with a CD4 count 100–200, and [
] those with a CD4 count 100–200, and [
 ] those with a CD4 count 200–250.
] those with a CD4 count 200–250.
 ] those who do not own their own home and pay greater than the median rent, and [
] those who do not own their own home and pay greater than the median rent, and [
 ] those who do not own their own home and pay less than the median rent.
] those who do not own their own home and pay less than the median rent.
 ] women who did not state a desire for additional children and were on hormonal contraceptives at enrollment, and [
] women who did not state a desire for additional children and were on hormonal contraceptives at enrollment, and [
 ] women who stated a desire for additional children and were on hormonal contraceptives at enrollment. b: Cumulative incidence of pregnancy among women comparing [▬] the period before ART initiation to [
] women who stated a desire for additional children and were on hormonal contraceptives at enrollment. b: Cumulative incidence of pregnancy among women comparing [▬] the period before ART initiation to [
 ] the period after ART initiation.
] the period after ART initiation.References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Vittinghoff E, Scheer S, O’Malley P, Colfax G, Holmberg SD, Buchbinder SP. Combination antiretroviral therapy and recent declines in AIDS incidence and mortality. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:717–720. - PubMed
-
- Attia S, Egger M, Muller M, Zwahlen M, Low N. Sexual transmission of HIV according to viral load and antiretroviral therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS. 2009;23:1397–1404. - PubMed
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. AIDS epidemic update. 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

