Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of sublingual immunotherapy in natural rubber latex allergic patients
- PMID: 21827704
- PMCID: PMC3175458
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-191
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of sublingual immunotherapy in natural rubber latex allergic patients
Abstract
Background: Natural rubber latex allergy is a common and unsolved health problem. Since the avoidance of exposure is very difficult, immunotherapy is strongly recommended, but before its use in patients, it is essential to prove the efficacy and safety of extracts.The aim of the present randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of latex sublingual immunotherapy in adult patients undergoing permanent latex avoidance.
Methods: Twenty-eight adult latex-allergic patients (5 males and 23 females), with mean age of 39 years (range 24-57) were randomized to receive a commercial latex-sublingual immunotherapy or placebo during one year, followed by another year of open, active therapy. The following outcomes were measured at baseline and at the end of first and second year of follow-up: skin prick test, gloves-use score, conjunctival challenge test, total and specific IgE, basophil activation test, and adverse reactions monitoring.
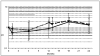
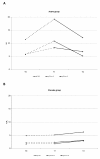
Results: No significant difference in any of the efficacy in vivo variables was observed between active and placebo groups at the end of the placebo-controlled phase, nor when each group was compared with their baseline values at the end of the two year-study. An improvement in the average percentage of basophils activated was observed. During the induction phase, 4 reactions in the active group and 5 in the placebo group were recorded. During the maintenance phase, two patients dropped out due to pruritus and to acute dermatitis respectively.
Conclusion: Further studies are needed to evaluate latex-sublingual immunotherapy, since efficacy could not be demonstrated in adult patients with avoidance of the allergen.
Trial registration number: ACTRN12611000543987.
Figures

References
-
- Carrillo T, Blanco C, Quiralte J, Castillo R, Cuevas M, Rodriguez de Castro F. Prevalence of latex allergy among greenhouse workers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96(5 Pt 1):699–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

