Stress tolerance to stress escape in plants: role of the OXS2 zinc-finger transcription factor family
- PMID: 21829164
- PMCID: PMC3173794
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.270
Stress tolerance to stress escape in plants: role of the OXS2 zinc-finger transcription factor family
Abstract
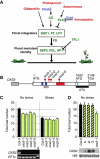
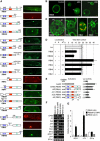
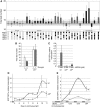
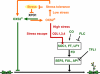
During dire conditions, the channelling of resources into reproduction ensures species preservation. This strategy of survival through the next generation is particularly important for plants that are unable to escape their environment but can produce hardy seeds. Here, we describe the multiple roles of OXIDATIVE STRESS 2 (OXS2) in maintaining vegetative growth, activating stress tolerance, or entering into stress-induced reproduction. In the absence of stress, OXS2 is cytoplasmic and is needed for vegetative growth; in its absence, the plant flowers earlier. Upon stress, OXS2 is nuclear and is needed for stress tolerance; in its absence, the plant is stress sensitive. OXS2 can activate its own gene and those of floral integrator genes, with direct binding to the floral integrator promoter SOC1. Stress-induced SOC1 expression and stress-induced flowering are impaired in mutants with defects in OXS2 and three of the four OXS2-like paralogues. The autoactivation of OXS2 may be a commensurate response to the stress intensity, stepping up from a strategy based on tolerating the effects of stress to one of escaping the stress via reproduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T (2005) FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309: 1052–1056 - PubMed
-
- An H, Roussot C, Suarez-Lopez P, Corbesier L, Vincent C, Pineiro M, Hepworth S, Mouradov A, Justin S, Turnbull C, Coupland G (2004) CONSTANS acts in the phloem to regulate a systemic signal that induces photoperiodic flowering of Arabidopsis. Development 131: 3615–3626 - PubMed
-
- Araki T (2001) Transition from vegetative to reproductive phase. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4: 63–68 - PubMed
-
- Blanvillain R, Kim JH, Wu S, Lima A, Ow DW (2009) OXIDATIVE STRESS 3 is a chromatin-associated factor involved in tolerance to heavy metals and oxidative stress. Plant J 57: 654–665 - PubMed
-
- Blazquez MA, Ahn JH, Weigel D (2003) A thermosensory pathway controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 33: 168–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

