The effect of sustained compression on oxygen metabolic transport in the intervertebral disc decreases with degenerative changes
- PMID: 21829341
- PMCID: PMC3150290
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002112
The effect of sustained compression on oxygen metabolic transport in the intervertebral disc decreases with degenerative changes
Abstract
Intervertebral disc metabolic transport is essential to the functional spine and provides the cells with the nutrients necessary to tissue maintenance. Disc degenerative changes alter the tissue mechanics, but interactions between mechanical loading and disc transport are still an open issue. A poromechanical finite element model of the human disc was coupled with oxygen and lactate transport models. Deformations and fluid flow were linked to transport predictions by including strain-dependent diffusion and advection. The two solute transport models were also coupled to account for cell metabolism. With this approach, the relevance of metabolic and mechano-transport couplings were assessed in the healthy disc under loading-recovery daily compression. Disc height, cell density and material degenerative changes were parametrically simulated to study their influence on the calculated solute concentrations. The effects of load frequency and amplitude were also studied in the healthy disc by considering short periods of cyclic compression. Results indicate that external loads influence the oxygen and lactate regional distributions within the disc when large volume changes modify diffusion distances and diffusivities, especially when healthy disc properties are simulated. Advection was negligible under both sustained and cyclic compression. Simulating degeneration, mechanical changes inhibited the mechanical effect on transport while disc height, fluid content, nucleus pressure and overall cell density reductions affected significantly transport predictions. For the healthy disc, nutrient concentration patterns depended mostly on the time of sustained compression and recovery. The relevant effect of cell density on the metabolic transport indicates the disturbance of cell number as a possible onset for disc degeneration via alteration of the metabolic balance. Results also suggest that healthy disc properties have a positive effect of loading on metabolic transport. Such relation, relevant to the maintenance of the tissue functional composition, would therefore link disc function with disc nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



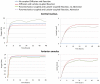
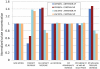



References
-
- Iatridis JC, Setton La, Foster RJ, Rawlins Ba, Weidenbaum M, et al. Degeneration affects the anisotropic and nonlinear behaviors of human anulus fibrosus in compression. J Biomech. 1998;31:535–544. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9755038. - PubMed
-
- Adams MA, Dolan P, McNally DS. The internal mechanical functioning of intervertebral discs and articular cartilage, and its relevance to matrix biology. Matrix Biol. 2009;28:384–389. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19586615. Accessed 18 Oct 2010. - PubMed
-
- Vernon-Roberts B, Moore RJ, Fraser RD. The natural history of age-related disc degeneration: the influence of age and pathology on cell populations in the L4-L5 disc. Spine. 2008;33:2767–2773. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19050583. - PubMed
-
- Urban JPG, Smith S, Fairbank JCT. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine. 2004;29:2700–2709. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15564919. - PubMed
-
- Arun R, Freeman B, Scammell B, McNally D, Cox E, et al. 2009 ISSLS Prize Winner: What Influence Does Sustained Mechanical Load Have on Diffusion in the Human Intervertebral Disc?: An In Vivo Study Using Serial Postcontrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Spine. 2009;34:2324–2337. Available: http://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Abstract/2009/10010/2009_ISSLS_Priz.... Accessed 14 Oct 2010. - PubMed

