Multiple ATR-Chk1 pathway proteins preferentially associate with checkpoint-inducing DNA substrates
- PMID: 21829571
- PMCID: PMC3146532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022986
Multiple ATR-Chk1 pathway proteins preferentially associate with checkpoint-inducing DNA substrates
Abstract
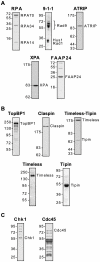
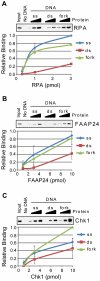
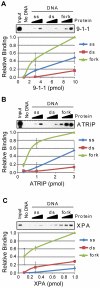
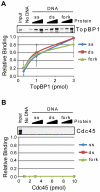
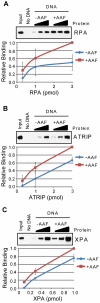
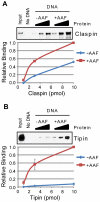
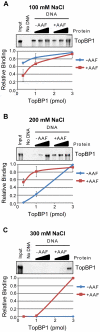
The ATR-Chk1 DNA damage checkpoint pathway is a critical regulator of the cellular response to DNA damage and replication stress in human cells. The variety of environmental, chemotherapeutic, and carcinogenic agents that activate this signal transduction pathway do so primarily through the formation of bulky adducts in DNA and subsequent effects on DNA replication fork progression. Because there are many protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions proposed to be involved in activation and/or maintenance of ATR-Chk1 signaling in vivo, we systematically analyzed the association of a number of ATR-Chk1 pathway proteins with relevant checkpoint-inducing DNA structures in vitro. These DNA substrates included single-stranded DNA, branched DNA, and bulky adduct-containing DNA. We found that many checkpoint proteins show a preference for single-stranded, branched, and bulky adduct-containing DNA in comparison to undamaged, double-stranded DNA. We additionally found that the association of checkpoint proteins with bulky DNA damage relative to undamaged DNA was strongly influenced by the ionic strength of the binding reaction. Interestingly, among the checkpoint proteins analyzed the checkpoint mediator proteins Tipin and Claspin showed the greatest differential affinity for checkpoint-inducing DNA structures. We conclude that the association and accumulation of multiple checkpoint proteins with DNA structures indicative of DNA damage and replication stress likely contribute to optimal ATR-Chk1 DNA damage checkpoint responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Reardon JT, Sancar A. Nucleotide excision repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2005;79:183–235. - PubMed
-
- Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Linn S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:39–85. - PubMed
-
- Liu P, Barkley LR, Day T, Bi X, Slater DM, et al. The Chk1-mediated S-phase checkpoint targets initiation factor Cdc45 via a Cdc25A/Cdk2-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(41):30631–30644. 10.1074/jbc.M602982200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

