High-resolution description of antibody heavy-chain repertoires in humans
- PMID: 21829618
- PMCID: PMC3150326
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022365
High-resolution description of antibody heavy-chain repertoires in humans
Abstract
Antibodies' protective, pathological, and therapeutic properties result from their considerable diversity. This diversity is almost limitless in potential, but actual diversity is still poorly understood. Here we use deep sequencing to characterize the diversity of the heavy-chain CDR3 region, the most important contributor to antibody binding specificity, and the constituent V, D, and J segments that comprise it. We find that, during the stepwise D-J and then V-DJ recombination events, the choice of D and J segments exert some bias on each other; however, we find the choice of the V segment is essentially independent of both. V, D, and J segments are utilized with different frequencies, resulting in a highly skewed representation of VDJ combinations in the repertoire. Nevertheless, the pattern of segment usage was almost identical between two different individuals. The pattern of V, D, and J segment usage and recombination was insufficient to explain overlap that was observed between the two individuals' CDR3 repertoires. Finally, we find that while there are a near-infinite number of heavy-chain CDR3s in principle, there are about 3-9 million in the blood of an adult human being.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
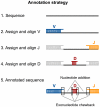
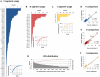
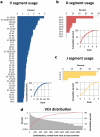
References
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

