MicroRNA 144 impairs insulin signaling by inhibiting the expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 21829658
- PMCID: PMC3148231
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022839
MicroRNA 144 impairs insulin signaling by inhibiting the expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2011;6(9). doi: 10.1371/annotation/698b7123-174f-4a09-95c9-fd6f5017d622 doi: 10.1371/annotation/698b7123-174f-4a09-95c9-fd6f5017d622
Abstract
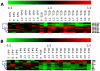
Background: Dysregulation of microRNA (miRNA) expression in various tissues and body fluids has been demonstrated to be associated with several diseases, including Type 2 Diabetes mellitus (T2D). Here, we compare miRNA expression profiles in different tissues (pancreas, liver, adipose and skeletal muscle) as well as in blood samples from T2D rat model and highlight the potential of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of T2D. In parallel, we have examined the expression profiles of miRNAs in blood samples from Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) and T2D male patients.
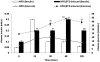
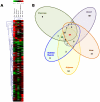
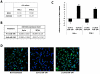
Methodology/principal findings: Employing miRNA microarray and stem-loop real-time RT-PCR, we identify four novel miRNAs, miR-144, miR-146a, miR-150 and miR-182 in addition to four previously reported diabetes-related miRNAs, miR-192, miR-29a, miR-30d and miR-320a, as potential signature miRNAs that distinguished IFG and T2D. Of these microRNAs, miR-144 that promotes erythropoiesis has been found to be highly up-regulated. Increased circulating level of miR-144 has been found to correlate with down-regulation of its predicted target, insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) at both mRNA and protein levels. We could also experimentally demonstrate that IRS1 is indeed the target of miR-144.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that peripheral blood microRNAs can be developed as unique biomarkers that are reflective and predictive of metabolic health and disorder. We have also identified signature miRNAs which could possibly explain the pathogenesis of T2D and the significance of miR-144 in insulin signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





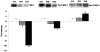
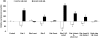

References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Janowski BA, Younger ST, Hardy DB, Ram R, Huffman KE, et al. Activating gene expression in mammalian cells with promoter-targeted duplex RNAs. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:166–173. - PubMed
-
- Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA. Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science. 2007;318:1931–1934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

