Highly active antiretroviral therapy in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus increases CD40 ligand expression and IL-12 production in cells ex vivo
- PMID: 21830900
- PMCID: PMC3154396
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2010.0142
Highly active antiretroviral therapy in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus increases CD40 ligand expression and IL-12 production in cells ex vivo
Abstract
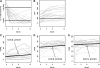
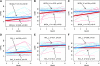
Highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) restores CD4(+) T-cell numbers in the periphery; however, its efficacy in restoring functional immunity is not fully elucidated. Here we evaluated longitudinal changes in the expression of several key markers of T-cell activation, namely CD40 ligand (CD154), OX40 (CD134), or CD69, after anti-CD3/CD28 activation, as well as levels of IL-12 production after Staphylococcus aureus Cowan stimulation in 28 HIV-infected adult patients. Patients were followed up to 12 mo post-HAART initiation. Viral burdens and CD4 cell counts were measured at the same time points. A control group of 15 HIV-uninfected adult subjects was included for comparison. Significant increases in CD40L and OX40 expression, but not of CD69 expression, were observed over time in the overall patient population, and more particularly in patients with baseline CD4 counts lower than or equal to 200 cells/μL, or those with baseline viral loads lower than or equal to 10(5) RNA copies/mL. Similar increases were seen for IL-12 production. Viral loads were inversely associated with CD40L expression or IL-12 production in a mixed linear model analysis, while CD4 counts were directly associated. CD40L expression and IL-12 production were significantly correlated. In conclusion, HAART-mediated control of viral replication led to partial restoration of CD40L upregulation/expression, and to increased IL-12 production, but the magnitude of the response depended on the baseline characteristics of the treated patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased CD40 ligand induction in CD4 T cells and dysregulated IL-12 production during HIV infection.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Aug;117(2):335-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00987.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10444266 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic immune activation in HIV-1 infection contributes to reduced interferon alpha production via enhanced CD40:CD40 ligand interaction.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033925. Epub 2012 Mar 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470494 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 ligand dysregulation in HIV infection: HIV glycoprotein 120 inhibits signaling cascades upstream of CD40 ligand transcription.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 15;172(4):2678-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2678. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14764743
-
Levels of soluble CD40 ligand (CD154) in serum are increased in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients and correlate with CD4(+) T-cell counts.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 May;9(3):558-61. doi: 10.1128/cdli.9.3.558-561.2002. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11986259 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biological assessment methods and understanding the course of the HIV infection.APMIS Suppl. 2003;(114):1-37. APMIS Suppl. 2003. PMID: 14626050 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunological cell type characterization and Th1-Th17 cytokine production in a mouse model of Gaucher disease.Mol Genet Metab. 2012 Jul;106(3):310-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.04.020. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Mol Genet Metab. 2012. PMID: 22595426 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Success in Trypanosoma cruzi Infection Is Predicted by Early Changes in Serially Monitored Parasite-Specific T and B Cell Responses.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Apr 29;10(4):e0004657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004657. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27128444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel JB. Kumar A. Parato K, et al. Improvement in cell-mediated immune function during potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus therapy with ritonavir plus saquinavir. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:898–904. - PubMed
-
- Angel JB. Parato KG. Kumar A, et al. Progressive human immunodeficiency virus-specific immune recovery with prolonged viral suppression. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:546–554. - PubMed
-
- Battegay M. Nuesch R. Hirschel B. Kaufmann GR. Immunological recovery and antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1 infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:280–287. - PubMed
-
- Bebell LM. Passmore JA. Williamson C, et al. Relationship between levels of inflammatory cytokines in the genital tract and CD4+ cell counts in women with acute HIV-1 infection. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:710–714. - PubMed
-
- Bocchino M. Ledru E. Debord T. Gougeon ML. Increased priming for interleukin-12 and tumour necrosis factor alpha in CD64 monocytes in HIV infection: modulation by cytokines and therapy. AIDS. 2001;15:1213–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

