Effect of emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance on intrinsic expression of P-glycoprotein phenotype in corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 21830912
- PMCID: PMC3235346
- DOI: 10.1089/jop.2011.0076
Effect of emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance on intrinsic expression of P-glycoprotein phenotype in corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: Multidrug resistance (MDR) represents a major obstacle to the success of antimicrobial fluoroquinolone (FQ) therapy. MDR-associated efflux protein pumps antimicrobial agents out of the corneal cells, leading to suboptimal eradication of microbes. This article examines whether long-term FQ (levofloxacin, ofloxacin, and gatifloxacin) therapy can modify the MDR phenotype (P-glycoprotein [P-gp]) on corneal epithelial cells (Statens Seruminstitut Rabbit Cornea [SIRC]).
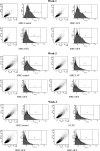
Methods: To study the effect of FQ, SIRC cells without any exposure to FQ (control) were compared with the cells exposed to ofloxacin, levofloxacin, and gatifloxacin at a concentration of 10 μg/mL for 3 weeks. Efflux activity of P-gp was assessed by in vitro uptake studies (fluorescent and radioactive), flow cytometry, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results: In the presence of FQ, elevated P-gp expression was noted with uptake, flow cytometry, and qRT-PCR analyses. This study confirms that long-term exposure to antibiotics, particularly FQ, can induce overexpression of P-gp efflux transporter present on the corneal cells. P-gp overexpression is commonly noticed in anticancer drug resistance cell lines; however, for the first time, this report describes overexpression of P-gp due to FQ exposure.
Conclusions: Based on this result, it is suggested that strategies should be developed and implemented not only to overcome resistance to ocular pathogen but also to FQ-induced cellular resistance.
Figures


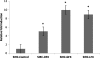
Similar articles
-
Molecular evidence and functional expression of P-glycoprotein (MDR1) in human and rabbit cornea and corneal epithelial cell lines.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Jul;44(7):2909-18. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-1142. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12824231
-
Molecular evidence and functional expression of a novel drug efflux pump (ABCC2) in human corneal epithelium and rabbit cornea and its role in ocular drug efflux.Int J Pharm. 2007 May 4;336(1):12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.11.031. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17156953 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of multidrug resistance associated protein 5 (MRP5) on cornea and its role in drug efflux.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Apr;25(2):121-32. doi: 10.1089/jop.2008.0084. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19323627 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistance: retrospect and prospects in anti-cancer drug treatment.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1859-76. doi: 10.2174/092986706777585077. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842198 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein as multidrug transporter: a critical review of current multidrug resistant cell lines.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 7;1139(3):169-83. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90131-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992. PMID: 1352705 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial localization of P-glycoprotein and peptide transporters in corneal epithelial cells--novel strategies for intracellular drug targeting.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Jan;106:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23116562 Free PMC article.
-
Prodrug strategies in ocular drug delivery.Med Chem. 2012 Jul;8(4):753-68. doi: 10.2174/157340612801216283. Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22530907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of polysaccharide of dendrobium candidum on proliferation and apoptosis of human corneal epithelial cells in high glucose.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Aug;96(32):e7773. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007773. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28796073 Free PMC article.
-
Transporter-targeted lipid prodrugs of cyclic cidofovir: a potential approach for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis.J Pharm Sci. 2012 Sep;101(9):3249-63. doi: 10.1002/jps.23140. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 22499243 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in retinal diseases.Curr Eye Res. 2011 Dec;36(12):1069-77. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2011.607536. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Curr Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21978133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

