Statin-induced apoptosis via the suppression of ERK1/2 and Akt activation by inhibition of the geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate biosynthesis in glioblastoma
- PMID: 21831290
- PMCID: PMC3163617
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-74
Statin-induced apoptosis via the suppression of ERK1/2 and Akt activation by inhibition of the geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate biosynthesis in glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Statins are inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. The inhibition of this key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway leads to suppression of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. However, the molecular mechanism of apoptosis induction by statins is not well understood in glioblastoma. In the present study, we attempted to elucidate the mechanism by which statins induce apoptosis in C6 glioma cells.
Methods: The cytotoxicity of statins toward the C6 glioma cells were evaluated using a cell viability assay. The enzyme activity of caspase-3 was determined using activity assay kits. The effects of statins on signal transduction molecules were determined by western blot analyses.
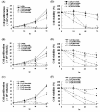
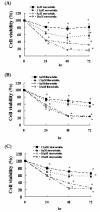
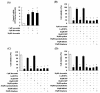
Results: We found that statins inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in these cells. We also observed an increase in caspase-3 activity. The apoptosis induced by statins was not inhibited by the addition of farnesyl pyrophosphate, squalene, ubiquinone, and isopentenyladenine, but by geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate (GGPP). Furthermore, statins decreased the levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and Akt.
Conclusions: These results suggest that statins induce apoptosis when GGPP biosynthesis is inhibited and consequently decreases the level of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Akt. The results of this study also indicate that statins could be used as anticancer agents in glioblastoma.
Figures


References
-
- Tsubaki M, Yamazoe Y, Yanae M, Satou T, Itoh T, Kaneko J, Kidera Y, Moriyama K, Nishida S. Blockade of the Ras/MEK/ERK and Ras/PI3K/Akt pathways by statins reduces the expression of bFGF, HGF, and TGF-β as angiogenic factors in mouse osteosarcoma. Cytokine. 2011;54:100–107. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.01.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

