Prostaglandin E2 regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion through the EP4 receptor-Rap GTPase signal transduction pathway
- PMID: 21832044
- PMCID: PMC3190815
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187344
Prostaglandin E2 regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion through the EP4 receptor-Rap GTPase signal transduction pathway
Abstract
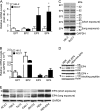
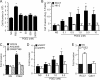
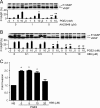
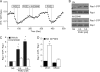
Prognosis for patients with early stage kidney cancer has improved, but the treatment options for patients with locally advanced disease and metastasis remain few. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate invasion and metastasis is critical for developing successful therapies to treat these patients. Proinflammatory prostaglandin E(2) plays an important role in cancer initiation and progression via activation of cognate EP receptors that belong to the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors. Here we report that prostaglandin E(2) promotes renal cancer cell invasion through a signal transduction pathway that encompasses EP4 and small GTPase Rap. Inactivation of Rap signaling with Rap1GAP, like inhibition of EP4 signaling with ligand antagonist or knockdown with shRNA, reduces the kidney cancer cell invasion. Human kidney cells evidence increased EP4 and decreased Rap1GAP expression levels in the malignant compared with benign samples. These results support the idea that targeted inhibition of EP4 signaling and restoration of Rap1GAP expression constitute a new strategy to control kidney cancer progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PGE2 promotes renal carcinoma cell invasion through activated RalA.Oncogene. 2013 Mar 14;32(11):1408-15. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.161. Epub 2012 May 14. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22580611 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1GAP regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion.Cancer Lett. 2012 Jul 1;320(1):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.022. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22266190 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 promotes lung cancer cell migration via EP4-betaArrestin1-c-Src signalsome.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Apr;8(4):569-77. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0511. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20353998 Free PMC article.
-
EP4 as a Therapeutic Target for Aggressive Human Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 29;19(4):1019. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041019. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29596308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EP4 receptor as a novel promising therapeutic target in colon cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Dec;216(12):153247. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153247. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33190014 Review.
Cited by
-
Arachidonic acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in AKI-to-CKD transition.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1365802. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1365802. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38523633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EMT induction in normal breast epithelial cells by COX2-expressing fibroblasts.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 May 22;23(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02227-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40405218 Free PMC article.
-
Development and external validation of a predictive model for lung metastases in kidney cancer based on clinical and laboratory features.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Aug 14;25(1):293. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01839-0. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40810966 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and cancer.Cell Biosci. 2013 Feb 6;3(1):8. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-3-8. Cell Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23388178 Free PMC article.
-
The role of metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 31;14:1402351. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1402351. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38884097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Thun M. J. (2009) CA Cancer J. Clin. 59, 225–249 - PubMed
-
- Biswas S., Eisen T. (2009) Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 6, 478–487 - PubMed
-
- Young A. N., Dale J., Yin-Goen Q., Harris W. B., Petros J. A., Datta M. W., Wang M. D., Marshall F. F., Amin M. B. (2006) Urology 67, 873–880 - PubMed
-
- Schlesinger-Raab A., Treiber U., Zaak D., Hölzel D., Engel J. (2008) Eur. J. Cancer 44, 2485–2495 - PubMed
-
- Murai M., Oya M. (2004) Curr. Opin. Urol. 14, 229–233 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

