Interaction studies between the chloroplast signal recognition particle subunit cpSRP43 and the full-length translocase Alb3 reveal a membrane-embedded binding region in Alb3 protein
- PMID: 21832051
- PMCID: PMC3186405
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.250746
Interaction studies between the chloroplast signal recognition particle subunit cpSRP43 and the full-length translocase Alb3 reveal a membrane-embedded binding region in Alb3 protein
Abstract
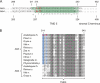
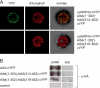
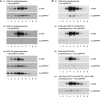
Posttranslational targeting of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a,b-binding proteins depends on the function of the chloroplast signal recognition particle, its receptor cpFtsY, and the translocase Alb3. The thylakoid membrane protein Alb3 of Arabidopsis chloroplasts belongs to the evolutionarily conserved YidC/Oxa1/Alb3 protein family; the members of this family facilitate the insertion, folding, and assembly of membrane proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Here, we analyzed the interaction sites of full-length Alb3 with the cpSRP pathway component cpSRP43 by using in vitro and in vivo studies. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation and Alb3 proteoliposome studies showed that the interaction of cpSRP43 is dependent on a binding domain in the C terminus of Alb3 as well as an additional membrane-embedded binding site in the fifth transmembrane domain (TMD5) of Alb3. The C-terminal binding domain was mapped to residues 374-388, and the binding domain within TMD5 was mapped to residues 314-318 located close to the luminal end of TMD5. A direct binding between cpSRP43 and these binding motifs was shown by pepspot analysis. Further studies using blue-native gel electrophoresis revealed that full-length Alb3 is able to form dimers. This finding and the identification of a membrane-embedded cpSRP43 binding site in Alb3 support a model in which cpSRP43 inserts into a dimeric Alb3 translocation pore during cpSRP-dependent delivery of light-harvesting chlorophyll a,b-binding proteins.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The C terminus of the Alb3 membrane insertase recruits cpSRP43 to the thylakoid membrane.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5954-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.084996. Epub 2009 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20018841 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic cpSRP43-Albino3 interaction mediates translocase regulation of chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP)-targeting components.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):34220-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.160093. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20729200 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between the cpSRP pathway components, the substrate LHCP and the translocase Alb3: an in vivo and in vitro study.FEBS Lett. 2010 Oct 8;584(19):4138-44. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.08.053. Epub 2010 Sep 7. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20828566
-
Component interactions, regulation and mechanisms of chloroplast signal recognition particle-dependent protein transport.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;89(12):965-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.06.020. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20709425 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of SRP-dependent light-harvesting protein transport to the thylakoid membrane in plants.Photosynth Res. 2018 Dec;138(3):303-313. doi: 10.1007/s11120-018-0544-6. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Photosynth Res. 2018. PMID: 29956039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Making proteins green; biosynthesis of chlorophyll-binding proteins in cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res. 2014 Feb;119(1-2):223-32. doi: 10.1007/s11120-013-9797-2. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Photosynth Res. 2014. PMID: 23377990 Review.
-
GET3B is involved in chloroplast biogenesis and interacts with the thylakoidal ALB3 and ALB4 insertases.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Apr 29;44(5):108. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03500-2. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40299103 Free PMC article.
-
The extreme Albino3 (Alb3) C terminus is required for Alb3 stability and function in Arabidopsis thaliana.Planta. 2015 Sep;242(3):733-46. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2352-y. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Planta. 2015. PMID: 26105652
-
The role of chloroplast SRP54 domains and its C-terminal tail region in post- and co-translational protein transport in vivo.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 27;75(18):5734-5749. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae293. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38989593 Free PMC article.
-
OsALB3 Is Required for Chloroplast Development by Promoting the Accumulation of Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll-Binding Proteins in Rice.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;12(23):4003. doi: 10.3390/plants12234003. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuhn A., Stuart R., Henry R., Dalbey R. E. (2003) Trends Cell Biol. 13, 510–516 - PubMed
-
- Luirink J., Samuelsson T., de Gier J. W. (2001) FEBS Lett. 501, 1–5 - PubMed
-
- Wang P., Dalbey R. E. (2011) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 866–875 - PubMed
-
- du Plessis D. J., Nouwen N., Driessen A. J. (2011) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 851–865 - PubMed
-
- Nouwen N., Driessen A. J. (2002) Mol. Microbiol. 44, 1397–1405 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

