An AP2 domain-containing gene, ESE1, targeted by the ethylene signaling component EIN3 is important for the salt response in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 21832142
- PMCID: PMC3192559
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.179028
An AP2 domain-containing gene, ESE1, targeted by the ethylene signaling component EIN3 is important for the salt response in Arabidopsis
Abstract
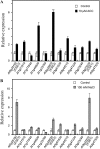
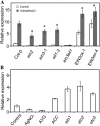
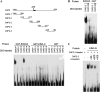
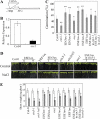
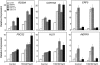
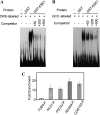
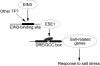
Accumulating investigations reveal that ethylene signaling is involved in the salt response in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and it has been reported that overexpression of a number of ethylene response factor (ERF) genes enhances salt tolerance; however, transcriptional regulation of the ethylene signal component ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 (EIN3) in the salt response has not been clearly defined. Consulting microarray data and transcriptional confirmations showed that three of the ERF genes were ethylene and salt inducible, named ESE1 to ESE3. Additionally, the expression of one of the ESE genes (ESE1) was suppressed in ein2, ein3-1, eil1-3, and ein3 eil1 but enhanced in EIN3-overexpressing (EIN3ox) lines. Inhibitors of ethylene biosynthesis, aminoethoxyvinylglycine, and ethylene action, AgNO₃, reduced the expression of ESE1, while ethylene overproduction eto mutants enhanced the expression of ESE1, indicating that ESE1 is an ethylene-modulated gene downstream of EIN3/EIL1. Further analyses with biochemical and molecular approaches revealed that EIN3 physically binds to the ESE1 promoter, demonstrating that ESE1 was one target of EIN3. ESE1 in turn binds to promoters of salt-related genes, such as RD29A and COR15A. Moreover, either EIN3ox or ESE1ox was sufficient to enhance transcript levels of salt-related genes and salt tolerance. In addition, ESE1ox in ein3 enhanced the salt response during seed germination and seedling development, demonstrating that ESE1 is genetically downstream of EIN3. Thus, the evidence in this report reveals that the transcriptional complex of EIN3-ESE1 is a crucial event in the salt response, thereby connecting the transcriptional regulation of EIN3 and the downstream ERF protein ESE1 in the salt response.
Figures


References
-
- Achard P, Cheng H, De Grauwe L, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J, Harberd NP. (2006) Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals. Science 311: 91–94 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal PK, Agarwal P, Reddy MK, Sopory SK. (2006) Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep 25: 1263–1274 - PubMed
-
- Bari R, Jones JD. (2009) Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol Biol 69: 473–488 - PubMed
-
- Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID. (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39: 205–207
-
- Beckers GJ, Spoel SH. (2006) Fine-tuning plant defence signalling: salicylate versus jasmonate. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 8: 1–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

