T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia
- PMID: 21832238
- PMCID: PMC3393096
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002842
T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia
Abstract
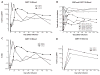
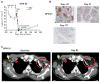
Tumor immunotherapy with T lymphocytes, which can recognize and destroy malignant cells, has been limited by the ability to isolate and expand T cells restricted to tumor-associated antigens. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) composed of antibody binding domains connected to domains that activate T cells could overcome tolerance by allowing T cells to respond to cell surface antigens; however, to date, lymphocytes engineered to express CARs have demonstrated minimal in vivo expansion and antitumor effects in clinical trials. We report that CAR T cells that target CD19 and contain a costimulatory domain from CD137 and the T cell receptor ζ chain have potent non-cross-resistant clinical activity after infusion in three of three patients treated with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The engineered T cells expanded >1000-fold in vivo, trafficked to bone marrow, and continued to express functional CARs at high levels for at least 6 months. Evidence for on-target toxicity included B cell aplasia as well as decreased numbers of plasma cells and hypogammaglobulinemia. On average, each infused CAR-expressing T cell was calculated to eradicate at least 1000 CLL cells. Furthermore, a CD19-specific immune response was demonstrated in the blood and bone marrow, accompanied by complete remission, in two of three patients. Moreover, a portion of these cells persisted as memory CAR(+) T cells and retained anti-CD19 effector functionality, indicating the potential of this major histocompatibility complex-independent approach for the effective treatment of B cell malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

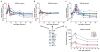

References
-
- Irving BA, Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor ζ chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991;64:891–901. - PubMed
-
- Uckun FM, Jaszcz W, Ambrus JL, Fauci AS, Gajl-Peczalska K, Song CW, Wick MR, Myers DE, Waddick K, Ledbetter JA. Detailed studies on expression and function of CD19 surface determinant by using B43 monoclonal antibody and the clinical potential of anti-CD19 immunotoxins. Blood. 1988;71:13–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

