Genetic architecture of declarative memory: implications for complex illnesses
- PMID: 21832260
- PMCID: PMC3545476
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858411415113
Genetic architecture of declarative memory: implications for complex illnesses
Abstract
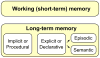
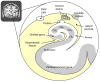
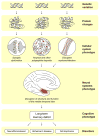
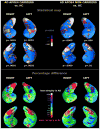
Why do memory abilities vary so greatly across individuals and cognitive domains? Although memory functions are highly heritable, what exactly is being genetically transmitted? Here we review evidence for the contribution of both common and partially independent inheritance of distinct aspects of memory function. We begin by discussing the assessment of long-term memory and its underlying neural and molecular basis. We then consider evidence for both specialist and generalist genes underlying individual variability in memory, indicating that carving memory into distinct subcomponents may yield important information regarding its genetic architecture. And finally we review evidence from both complex and single-gene disorders, which provide insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying the genetic basis of human memory function.
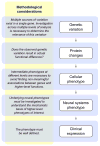
Figures




References
-
- Alarcon M, Plomin R, Fulker DW, Corley R, DeFries JC. Multivariate path analysis of specific cognitive abilities data at 12 years of age in the Colorado Adoption Project. Behav Genet. 1998;28:255–264. - PubMed
-
- Allen JS, Bruss J, Brown CK, Damasio H. Normal neuroanatomical variation due to age: the major lobes and a parcellation of the temporal region. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:1245–1260. discussion 1279–1282. - PubMed
-
- Almasy L. Quantitative risk factors as indices of alcoholism susceptibility. Ann Med. 2003;35:337–343. - PubMed
-
- Amaral D, Lavenex P. Hippocampal Neuroanatomy. In: Andersen P, Morris R, Amaral D, Bliss T, O’Keefe J, editors. The Hippocampus Book. Oxford University Press; 2006.
-
- Baare WF, Hulshoff Pol HE, Boomsma DI, Posthuma D, de Geus EJ, Schnack HG, van Haren NE, van Oel CJ, Kahn RS. Quantitative genetic modeling of variation in human brain morphology. Cereb Cortex. 2001;11:816–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01-MH080912-03/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R34 MH08929/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 LM009833/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078143/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RL1-DA024853/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080912/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH074644/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01-MH078143-06/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RL1-LM009833/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DA024853/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23-MH74644/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

