Seasonal effects on bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of six economically important brassica vegetables
- PMID: 21832972
- PMCID: PMC6264194
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16086816
Seasonal effects on bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of six economically important brassica vegetables
Abstract
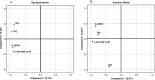
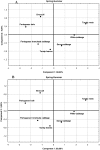
Research on natural and bioactive compounds is increasingly focused on their effects on human health, but there are unexpectedly few studies evaluating the relationship between climate and natural antioxidants. The aim of this study was analyze the biological role of six different Brassica vegetables (Brassica oleracea L. and Brassica rapa L.) as a natural source of antioxidant compounds. The antioxidant activity may be assigned to high levels of L-ascorbic acid, total phenolics and total flavonoids of each sample. The climate seasons affected directly the concentration of bioactive components and the antioxidant activity. Broccoli inflorescences and Portuguese kale showed high antioxidant activity in Spring-Summer whilst turnip leaves did so in Summer-Winter. The Brassica vegetables can provide considerable amounts of bioactive compounds and thus may constitute an important natural source of dietary antioxidants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Podsędek A. Natural antioxidants and antioxidant capacity of Brassica vegetables: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007;40:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2005.07.023. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

