Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition enhances the dopamine D1 receptor/PKA/DARPP-32 signaling cascade in frontal cortex
- PMID: 21833500
- PMCID: PMC3539205
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2436-8
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition enhances the dopamine D1 receptor/PKA/DARPP-32 signaling cascade in frontal cortex
Abstract
Rationale: Alteration of dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex, especially hypofunction of dopamine D1 receptors, contributes to psychotic symptoms and cognitive deficit in schizophrenia. D1 receptors signal through the cAMP/PKA second messenger cascade, which is modulated by phosphodiesterase (PDE) enzymes that hydrolyze and inactivate cyclic nucleotides. Though several PDEs are expressed in cortical neurons, the PDE4 enzyme family (PDE4A-D) has been implicated in the control of cognitive function. The best studied isoform, PDE4B, interacts with a schizophrenia susceptibility factor, disrupted in schizophrenia 1 (DISC1).
Objectives: We explore the control of mouse frontal cortex dopamine D1 receptor signaling and associated behavior by PDE4.
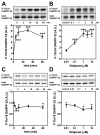
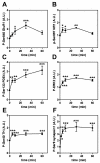
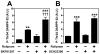
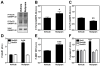
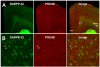
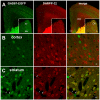
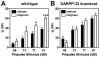
Results: Inhibition of PDE4 by rolipram induced activation of cAMP/PKA signaling in cortical slices and in vivo, leading to the phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and other postsynaptic and presynaptic PKA-substrates. Rolipram also enhanced DARPP-32 phosphorylation invoked by D1 receptor activation. Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated PDE4A, PDE4B, and PDE4D expression in DARPP-32-positive neurons in layer VI of frontal cortex, most likely in D1 receptor-positive, glutamatergic corticothalamic pyramidal neurons. Furthermore, the ability of rolipram treatment to improve the performance of mice in a sensorimotor gating test was DARPP-32-dependent.
Conclusions: PDE4, which is co-expressed with DARPP-32 in D1 receptor-positive cortical pyramidal neurons in layer VI, modulates the level of D1 receptor signaling and DARPP-32 phosphorylation in the frontal cortex, likely influencing cognitive function. These biochemical and behavioral actions of PDE4 inhibitors may contribute to the hypothesized antipsychotic actions of this class of compounds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles of PDE4 and PDE10A in the regulation of cAMP/PKA signaling in the striatum.J Neurosci. 2008 Oct 15;28(42):10460-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2518-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18923023 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic interactions of dopamine D1 and glutamate NMDA receptors in rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex: involvement of ERK1/2 signaling.Neuroscience. 2009 Nov 10;163(4):1135-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.056. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19647050
-
Glutamate Counteracts Dopamine/PKA Signaling via Dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 Ser-97 and Alteration of Its Cytonuclear Distribution.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 27;292(4):1462-1476. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.752402. Epub 2016 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27998980 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for targeting dopamine/DARPP-32 signaling in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Mar;21(3):259-272. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1279149. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28052701 Review.
-
PET measurements of cAMP-mediated phosphodiesterase-4 with (R)-[11C]rolipram.Curr Radiopharm. 2011 Jan;4(1):44-58. doi: 10.2174/1874471011104010044. Curr Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 22191614 Review.
Cited by
-
Striatal neurones have a specific ability to respond to phasic dopamine release.J Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;591(13):3197-214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.252197. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23551948 Free PMC article.
-
DISC1-ATF4 transcriptional repression complex: dual regulation of the cAMP-PDE4 cascade by DISC1.Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Aug;18(8):898-908. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.38. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23587879 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant-Negative Attenuation of cAMP-Selective Phosphodiesterase PDE4D Action Affects Learning and Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 9;21(16):5704. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165704. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784895 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 1b (PDE1B) Regulates Spatial and Contextual Memory in Hippocampus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb 7;12:21. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00021. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30792627 Free PMC article.
-
Dunce Phosphodiesterase Acts as a Checkpoint for Drosophila Long-Term Memory in a Pair of Serotonergic Neurons.Neuron. 2018 Apr 18;98(2):350-365.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.032. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29673482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert KA, Hemmings HC, Jr., Adamo AI, Potkin SG, Akbarian S, Sandman CA, Cotman CW, Bunney WE, Jr., Greengard P. Evidence for decreased DARPP-32 in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:705–12. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez R, Sette C, Yang D, Eglen RM, Wilhelm R, Shelton ER, Conti M. Activation and selective inhibition of a cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase, PDE-4D3. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;48:616–22. - PubMed
-
- Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: functional implications of multiple isoforms. [Review] Physiol. Reviews. 1995;75:725–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R43 MH067488/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH 090963/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH083711/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH090963/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH79710/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079710/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA010044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R44 MH067488/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH067488/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016672/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA020199/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA10044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083711/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA016672/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

