An integrated proteomic approach to identifying circulating biomarkers in high-risk neuroblastoma and their potential in relapse monitoring
- PMID: 21833997
- PMCID: PMC3685293
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201000089
An integrated proteomic approach to identifying circulating biomarkers in high-risk neuroblastoma and their potential in relapse monitoring
Abstract
Purpose: Despite intensive treatment regimens, overall survival for high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) is still poor. This is in part due to an inability to cure the disease once a patient has reached clinical relapse. Identifying plasma biomarkers of active disease may provide a way of relapse monitoring in HRNB.
Experimental design: In this study, we developed an integrated proteomic approach to identify plasma biomarkers for HRNB.
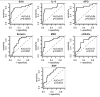
Results: We identified seven candidate biomarkers (SAA, APOA1, IL-6, EGF, MDC, sCD40L and Eotaxin) for HRNB. These biomarkers were then used to create a multivariate classifier of HRNB, which showed a specificity of 90% (95% confidence interval (CI), 73%, 98%), and a sensitivity of 81% (95%CI, 54%, 96%) for classifying HRNB in a training set. When evaluated on independent test samples, the classifier exhibited 86% accuracy (95% CI, 42%, 100%) of identifying diagnostic samples, and 86% accuracy (95% CI, 70%, 100%) of detecting post-diagnosis longitudinal samples that having active disease.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: Further validation of these biomarkers may improve patients' outcomes by developing a simple blood test for the detection of relapse prior to the development of clinically evident disease. Understanding the role of these biomarkers in immune surveillance of neuroblastoma may also provide a new direction of therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL. Lancet. 2007 Jun 23;369:2106–2120. - PubMed
-
- Matthay KK, Perez C, Seeger RC, Brodeur GM, Shimada H, Atkinson JB, Black CT, Gerbing R, Haase GM, Stram DO, Swift P, Lukens JN. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998;16:1256–1264. - PubMed
-
- Lau L. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2002;19:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Maris JM. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2005;17:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Lau L, Tai D, Weitzman S, Grant R, Baruchel S, Malkin D. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2004;26:227–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

