Carbofuran occupational dermal toxicity, exposure and risk assessment
- PMID: 21834090
- PMCID: PMC3378708
- DOI: 10.1002/ps.2270
Carbofuran occupational dermal toxicity, exposure and risk assessment
Abstract
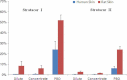
Background: Carbofuran is a carbamate insecticide that inhibits AChE. Although toxic by ingestion in mammals, it has low dermal toxicity, with relatively few confirmed worker illnesses. This risk assessment describes its time of onset, time to peak effect and time to recovery in rats using brain AChE inhibition in acute and 21 day dermal studies; in vitro rat/human relative dermal absorption for granular (5G) and liquid (4F) formulations; occupational exposure estimates using the Pesticide Handlers' Exposure Database and Agricultural Handlers' Exposure Database (PHED/AHED).
Results: The point of departure for acute risk calculation (BMDL(10)) was 6.7 mg kg(-1) day(-1) for brain AChE inhibition after 6 h exposure. In a 21 day study, the BMDL(10) was 6.8 mg kg(-1) day(-1), indicating reversibility. At 75 mg kg(-1) day(-1), time of onset was ≤ 30 min and time to peak effect was 6-12 h. Rat skin had ca tenfold greater dermal absorption of carbofuran (Furadan(®) 5G or 4F) than human skin. Exposure estimates for 5G in rice and 4F in ten crops had adequate margins of exposure (>100).
Conclusion: Rat dermal carbofuran toxicity was assessed in terms of dose and time-related inhibition of AChE. Comparative dermal absorption in rats was greater than in humans. Worker exposure estimates indicated acceptable risk for granular and liquid formulations of carbofuran.
Copyright © 2011 Society of Chemical Industry.
Figures




References
-
- Ecobichon DJ. Carbamate insecticides. In: Krieger RI, editor. Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. 2nd edition. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2001. pp. 1087–1106.
-
- Carbofuran. Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues, No. 196, pp. 12–14 (2009)
-
- The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- Edmiston S, Schneider F, Hernandez B, Fredrickson AS, Quan V. 1999. Exposure and illness following early reentry into a carbofuran-treated field. California EPA, HS-1779, 14 pp.
-
- Pesticide Handlers' Exposure Database [Online]. Available: www.exposuretf.com/Home/AHETF/AHETFDataDevelopment/PHED/tabid/100/Defaul... [2 April 2010]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

