Rationale and design of dal-PLAQUE: a study assessing efficacy and safety of dalcetrapib on progression or regression of atherosclerosis using magnetic resonance imaging and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- PMID: 21835280
- PMCID: PMC4047820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.05.006
Rationale and design of dal-PLAQUE: a study assessing efficacy and safety of dalcetrapib on progression or regression of atherosclerosis using magnetic resonance imaging and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
Abstract
dal-PLAQUE is a placebo-controlled multicenter study designed to assess the effect of dalcetrapib on imaging measures of plaque inflammation and plaque burden. dal-PLAQUE is a multimodality imaging study in the context of the large dal-HEART Program. Decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is linked to increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). Dalcetrapib, a compound that increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by modulating cholesteryl ester transfer protein, is being studied to assess if it can reduce the progression of atherosclerotic disease and thereby decrease cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Patients with CHD or CHD-risk equivalents were randomized to receive 600 mg dalcetrapib or placebo daily for 24 months, in addition to conventional lipid-lowering medication and other medications for cardiovascular risk factors. The primary outcomes are the effect of dalcetrapib on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography target-to-background ratio after 6 months and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plaque burden (wall area, wall thickness, total vessel area, and wall area/total vessel area ratio) after 12 months. Secondary objectives include positron emission tomography target-to-background ratio at 3 months and MRI plaque burden at 6 and 24 months; plaque composition at 6, 12, and 24 months; and aortic compliance at 6 months. A tertiary objective is to examine the dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI parameters of plaque neovascularization. In total, 189 subjects entered screening, and 130 were randomized. dal-PLAQUE will provide important information on the effects of dalcetrapib on markers of inflammation and atherosclerotic plaque burden and, thereby, on the safety of cholesteryl ester transfer protein modulation with dalcetrapib. Results are expected in 2011.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

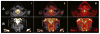
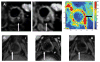
References
-
- Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular-disease— 4 prospective American studies. Circulation. 1989;79:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Quintao ECR, Cazita PM. Lipid transfer proteins: past, present and perspectives. Atherosclerosis. 2010;209:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Tomás M, Latorre G, Senti M, et al. The antioxidant function of high density lipoproteins: a new paradigm in atherosclerosis. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2004;57:557–69. - PubMed
-
- Klerkx AHEM, El Harchaoui K, van der Steeg WA, et al. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibition beyond raising high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels—pathways by which modulation of CETP activity may alter atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:706–15. - PubMed
-
- Thompson A, Di Angelantonio E, Sarwar N, et al. Association of cholesteryl ester transfer protein genotypes with CETP mass and activity, lipid levels, and coronary risk. JAMA. 2008;299:2777–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

