Serotonin 2C receptor activates a distinct population of arcuate pro-opiomelanocortin neurons via TRPC channels
- PMID: 21835345
- PMCID: PMC3184528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.06.012
Serotonin 2C receptor activates a distinct population of arcuate pro-opiomelanocortin neurons via TRPC channels
Abstract
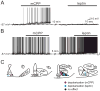
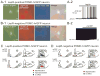
Serotonin 2C receptors (5-HT(2C)Rs) expressed by pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons of hypothalamic arcuate nucleus regulate food intake, energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism. However, the cellular mechanisms underlying the effects of 5-HT to regulate POMC neuronal activity via 5-HT(2C)Rs have not yet been identified. In the present study, we found the putative transient receptor potential C (TRPC) channels mediate the activation of a subpopulation of POMC neurons by mCPP (a 5-HT(2C)R agonist). Interestingly, mCPP-activated POMC neurons were found to be a distinct population from those activated by leptin. Together, our data suggest that 5-HT(2C)R and leptin receptors are expressed by distinct subpopulations of arcuate POMC neurons and that both 5-HT and leptin exert their actions in POMC neurons via TRPC channels.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


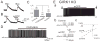

Similar articles
-
TrpC5 Mediates Acute Leptin and Serotonin Effects via Pomc Neurons.Cell Rep. 2017 Jan 17;18(3):583-592. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.072. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28099839 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor-mediated inhibition of the M-current in hypothalamic POMC neurons.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):E1399-406. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00565.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22436698 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor signaling in hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neurons: role in energy homeostasis in females.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;72(4):885-96. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.038083. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17622577
-
Functional heterogeneity of arcuate nucleus pro-opiomelanocortin neurons: implications for diverging melanocortin pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Apr;45(2):225-33. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8240-6. Epub 2012 Feb 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22328135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The arcuate nucleus as a conduit for diverse signals relevant to energy homeostasis.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001 Dec;25 Suppl 5:S63-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801913. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001. PMID: 11840218 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic plasticity in neuronal circuits regulating energy balance.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Oct;15(10):1336-42. doi: 10.1038/nn.3219. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23007188 Review.
-
From neuroanatomy to behavior: central integration of peripheral signals regulating feeding behavior.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Oct;15(10):1350-5. doi: 10.1038/nn.3217. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23007190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain regulation of energy balance and body weight.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013 Dec;14(4):387-407. doi: 10.1007/s11154-013-9261-9. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013. PMID: 23990408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose rapidly induces different forms of excitatory synaptic plasticity in hypothalamic POMC neurons.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 15;9(8):e105080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105080. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25127258 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular census of arcuate hypothalamus and median eminence cell types.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Mar;20(3):484-496. doi: 10.1038/nn.4495. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28166221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astrup A. Drug management of obesity-efficacy versus safety. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:288–290. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Dalgaard LT, Lee CE, Yu J, Funahashi H, Williams T, Ferreira M, Tang V, McGovern RA, Kenny CD, et al. Divergence of melanocortin pathways in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. Cell. 2005;123:493–505. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strubing C. The TRP ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:387–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK053301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024923/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK087780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061583/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK088423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK085330/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK53301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH061933/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK087780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RL1DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061933/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024923/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 DK081182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

