Selective p38α MAPK deletion in serotonergic neurons produces stress resilience in models of depression and addiction
- PMID: 21835346
- PMCID: PMC3155685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.06.011
Selective p38α MAPK deletion in serotonergic neurons produces stress resilience in models of depression and addiction
Abstract
Maladaptive responses to stress adversely affect human behavior, yet the signaling mechanisms underlying stress-responsive behaviors remain poorly understood. Using a conditional gene knockout approach, the α isoform of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) was selectively inactivated by AAV1-Cre-recombinase infection in specific brain regions or by promoter-driven excision of p38α MAPK in serotonergic neurons (by Slc6a4-Cre or ePet1-Cre) or astrocytes (by Gfap-CreERT2). Social defeat stress produced social avoidance (a model of depression-like behaviors) and reinstatement of cocaine preference (a measure of addiction risk) in wild-type mice, but not in mice having p38α MAPK selectively deleted in serotonin-producing neurons of the dorsal raphe nucleus. Stress-induced activation of p38α MAPK translocated the serotonin transporter to the plasma membrane and increased the rate of transmitter uptake at serotonergic nerve terminals. These findings suggest that stress initiates a cascade of molecular and cellular events in which p38α MAPK induces a hyposerotonergic state underlying depression-like and drug-seeking behaviors.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
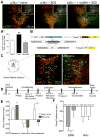


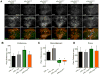


Comment in
-
Tracking down the molecular substrates of stress: new roles for p38α MAPK and kappa-opioid receptors.Neuron. 2011 Aug 11;71(3):383-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.018. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21835335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed BY, Chakravarthy S, Eggers R, Hermens WTJMC, Zhang JY, Niclou SP, Levelt C, Sablitzky F, Anderson PN, Lieberman AR, et al. Efficient delivery of Cre-recombinase to neurons in vivo and stable transduction of neurons using adeno-associated and lentiviral vectors. BMC Neurosci. 2004;5:4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ansorge MS, Zhou M, Lira A, Hen R, Gingrich JA. Early-life blockade of the 5-HT transporter alters emotional behavior in adult mice. Science. 2004;306:879–881. - PubMed
-
- Avgustinovich DF, Kovalenko IL. Formation of behavioral pathology in female C57BL/6J mice exposed to prolonged negative psychoemotional conditions. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2005;35:959–967. - PubMed
-
- Bal N, Figueras G, Vilaró MT, Suñol C, Artigas F. Antidepressant drugs inhibit a glial 5-hydroxytryptamine transporter in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;9(8):1728–1738. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

