Directing human embryonic stem cell differentiation by non-viral delivery of siRNA in 3D culture
- PMID: 21835461
- PMCID: PMC3313656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.057
Directing human embryonic stem cell differentiation by non-viral delivery of siRNA in 3D culture
Abstract
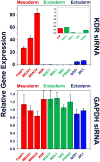
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) hold great potential as a resource for regenerative medicine. Before achieving therapeutic relevancy, methods must be developed to control stem cell differentiation. It is clear that stem cells can respond to genetic signals, such as those imparted by nucleic acids, to promote lineage-specific differentiation. Here we have developed an efficient system for delivering siRNA to hESCs in a 3D culture matrix using lipid-like materials. We show that non-viral siRNA delivery in a 3D scaffolds can efficiently knockdown 90% of GFP expression in GFP-hESCs. We further show that this system can be used as a platform for directing hESC differentiation. Through siRNA silencing of the KDR receptor gene, we achieve concurrent downregulation (60-90%) in genes representative of the endoderm germ layer and significant upregulation of genes representative of the mesoderm germ layer (27-90 fold). This demonstrates that siRNA can direct stem cell differentiation by blocking genes representative of one germ layer and also provides a particularly powerful means to isolate the endoderm germ layer from the mesoderm and ectoderm. This ability to inhibit endoderm germ layer differentiation could allow for improved control over hESC differentiation to desired cell types.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
R.L and D.G.A are consultants with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. R.L and D.G.A have sponsored research grants from Alnylam.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A high-throughput multiplexed screening assay for optimizing serum-free differentiation protocols of human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res. 2011 Mar;6(2):129-42. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Stem Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21169079
-
Intrinsic properties and external factors determine the differentiation bias of human embryonic stem cell lines.Cell Biol Int. 2010 Oct;34(10):1021-31. doi: 10.1042/CBI20100283. Cell Biol Int. 2010. PMID: 20586725
-
Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into endoderm without embryoid body formation.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e14146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014146. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21152387 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient derivation of human neuronal progenitors and neurons from pluripotent human embryonic stem cells with small molecule induction.J Vis Exp. 2011 Oct 28;(56):e3273. doi: 10.3791/3273. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22064669 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering tissue from human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Jun;12(3):709-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00228.x. Epub 2008 Jan 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18194458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterial-Based Approaches for Neural Regeneration.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jun 8;11(6):266. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11060266. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31181719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma membrane recovery kinetics of a microfluidic intracellular delivery platform.Integr Biol (Camb). 2014 Apr;6(4):470-5. doi: 10.1039/c3ib40215k. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Integr Biol (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24496115 Free PMC article.
-
The Delivery of RNA-Interference Therapies Based on Engineered Hydrogels for Bone Tissue Regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 May 12;8:445. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00445. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32478058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technologies for controlled, local delivery of siRNA.J Control Release. 2015 Nov 28;218:94-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.09.066. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26476177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimized delivery of siRNA into 3D tumor spheroid cultures in situ.Sci Rep. 2018 May 21;8(1):7952. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26253-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29785035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keller G. Embryonic stem cell differentiation: emergence of a new era in biology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2005;19(10):1129–55. - PubMed
-
- Wobus AM, Boheler KR. Embryonic stem cells: prospects for developmental biology and cell therapy. Physiol Rev. 2005;85(2):635–78. - PubMed
-
- Keller R, Davidson LA, Shook DR. How we are shaped: the biomechanics of gastrulation. Differentiation. 2003;71(3):171–205. - PubMed
-
- Zoldan J, Kraehenbuehl PT, Lytton-Jean AKR, Langer RS, Anderson DG. Tissue Engineering for Stem Cell Mediated Regenerative Medicine. In: Stein GS, Borowski M, Luong MX, Shi M-J, Smith KP, Vasquex P, editors. Human Stem Cell Technology & Biology. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2010. pp. 377–399.
-
- Hay DC, Sutherland L, Clark J, Burdon T. Oct-4 knockdown induces similar patterns of endoderm and trophoblast differentiation markers in human and mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22(2):225–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

