Evidence for a complex of transcription factor IIB with poly(A) polymerase and cleavage factor 1 subunits required for gene looping
- PMID: 21835917
- PMCID: PMC3190792
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.193870
Evidence for a complex of transcription factor IIB with poly(A) polymerase and cleavage factor 1 subunits required for gene looping
Abstract
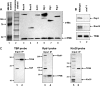
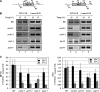
Gene looping, defined as the interaction of the promoter and the terminator regions of a gene during transcription, requires transcription factor IIB (TFIIB). We have earlier demonstrated association of TFIIB with the distal ends of a gene in an activator-dependent manner (El Kaderi, B., Medler, S., Raghunayakula, S., and Ansari, A. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 25015-25025). The presence of TFIIB at the 3' end of a gene required its interaction with cleavage factor 1 (CF1) 3' end processing complex subunit Rna15. Here, employing affinity chromatography and glycerol gradient centrifugation, we show that TFIIB associates with poly(A) polymerase and the entire CF1 complex in yeast cells. The factors required for general transcription such as TATA-binding protein, RNA polymerase II, and TFIIH are not a component of the TFIIB complex. This holo-TFIIB complex was resistant to MNase digestion. The complex was observed only in the looping-competent strains, but not in the looping-defective sua7-1 strain. The requirement of Rna15 in gene looping has been demonstrated earlier. Here we provide evidence that poly(A) polymerase (Pap1) as well as CF1 subunits Rna14 and Pcf11 are also required for loop formation of MET16 and INO1 genes. Accordingly, cross-linking of TFIIB to the 3' end of genes was abolished in the mutants of Pap1, Rna14, and Pcf11. We further show that in sua7-1 cells, where holo-TFIIB complex is not formed, the kinetics of activated transcription is altered. These results suggest that a complex of TFIIB, CF1 subunits, and Pap1 exists in yeast cells. Furthermore, TFIIB interaction with the CF1 complex and Pap1 is crucial for gene looping and transcriptional regulation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Gene looping is conferred by activator-dependent interaction of transcription initiation and termination machineries.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 11;284(37):25015-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007948. Epub 2009 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19602510 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of start site selection by RNA polymerase II: interplay between TFIIB and Ssl2/XPB helicase subunit of TFIIH.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 2;287(1):557-567. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.281576. Epub 2011 Nov 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22081613 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II plays an active role in the formation of gene loops through the Rpb4 subunit.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 26;47(17):8975-8987. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz597. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31304538 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the canonical role of TFIIB in eukaryotic transcription.Curr Genet. 2022 Feb;68(1):61-67. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01223-x. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Curr Genet. 2022. PMID: 34797379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Architectural and functional details of CF IA proteins involved in yeast 3'-end pre-mRNA processing and its significance for eukaryotes: A concise review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 15;193(Pt A):387-400. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.129. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34699898 Review.
Cited by
-
Role for gene looping in intron-mediated enhancement of transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 29;109(22):8505-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112400109. Epub 2012 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22586116 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interaction network revealed by quantitative proteomic analysis links TFIIB to multiple aspects of the transcription cycle.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2024 Jan 1;1872(1):140968. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2023.140968. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2024. PMID: 37863410 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Architecture Facilitates Intron-Mediated Enhancement of Transcription.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 21;8:669004. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.669004. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33968994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ssu72: a versatile protein with functions in transcription and beyond.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 18;11:1332878. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1332878. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38304578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP1 represses PAP and inhibits polyadenylation during heat shock.Mol Cell. 2013 Jan 10;49(1):7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23219533 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

